When discussing breast surgery procedures, it’s important to understand the various types available and their purposes. These may include breast augmentation, reduction, lift, reconstruction, or corrective surgeries. Each procedure aims to address specific concerns related to breast size, shape, symmetry, or post-mastectomy reconstruction. Patients often seek these surgeries for cosmetic enhancement, alleviation of physical discomfort, or reconstructive purposes after trauma or illness. Each procedure involves distinct techniques and considerations, ensuring personalized care and desired outcomes for individuals.
Exploring Breast Surgery Procedures
breast surgery procedures encompass various goals and motivations for individuals seeking these interventions. Here are insights into common goals and considerations:
Common Goals and Motivations:
- Cosmetic Enhancement:
- Breast Augmentation: Often pursued to increase breast size or enhance shape.
- Breast Lift: Aims to address sagging or drooping breasts, restoring a more youthful appearance.
- Breast Reduction: Targets alleviating discomfort or pain associated with excessively large breasts.
- Reconstructive or Corrective Purposes:
- Breast Reconstruction: Typically post-mastectomy, reconstructing breasts to restore appearance and confidence.
- Corrective Surgery: Addressing congenital issues, asymmetry, or irregularities for aesthetic or functional reasons.
Considerations Before Undergoing Surgery:
- Personal Health and Expectations:
- Medical Assessment: Evaluate overall health, discuss expectations, risks, and outcomes with a qualified surgeon.
- Realistic Expectations: Understand achievable results and recovery process, ensuring alignment with personal goals.
- Procedural Choices and Risks:
- Procedure Selection: Differentiate between augmentation, reduction, lift, or reconstruction; comprehend techniques, benefits, and limitations.
- Risks and Complications: Acknowledge potential risks like infection, scarring, or adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Emotional and Lifestyle Impact:
- Emotional Readiness: Acknowledge the emotional impact of altering one’s appearance; ensure mental preparedness.
- Lifestyle Changes: Consider post-operative recovery time, changes in physical activities, and ongoing care requirements.
- Consultation and Decision-Making:
- Consultation with Experts: Seek multiple consultations with experienced surgeons, understanding personalized options and recommendations.
- Informed Decision: Make an informed decision after thorough research, understanding risks, benefits, and realistic expectations.
Breast surgery procedures are highly personalized, requiring careful consideration and informed decisions aligned with individual goals and health circumstances. Consulting with a qualified professional is crucial to ensure the best possible outcome and satisfaction.
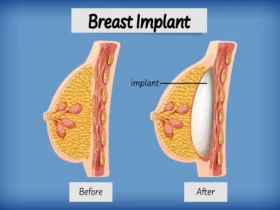
Breast Augmentation: Enhancing Breast Size
Breast augmentation, aimed at enhancing breast size, involves various types of implants and surgical techniques tailored to individual preferences and anatomical considerations.
Types of Breast Implants:
- 1. Saline Implants:
- Consist of a silicone shell filled with sterile saline (saltwater) solution.
- Adjustable in size during surgery.
- If ruptured, the saline is harmlessly absorbed by the body.
- 2. Silicone Gel Implants:
- Comprise a silicone shell filled with a cohesive silicone gel.
- Known for a more natural feel and appearance.
- Requires a slightly larger incision for placement.
- 3. Structured Implants:
- Incorporate an internal structure, enhancing shape and support.
- Utilize saline or silicone filling.
- Aim for a more natural contour and minimized rippling.
- 4. Gummy Bear Implants:
- Form-stable implants with a thicker silicone gel, maintaining shape even if the shell ruptures.
- Offer a teardrop shape, mimicking the natural breast contour.
Surgical Techniques:
- 1. Incision Placement:
- Inframammary: Incision made along the breast crease.
- Periareolar: Incision made around the areola’s edge.
- Transaxillary: Incision made in the armpit.
- Transumbilical: Rarely used; incision made near the navel.
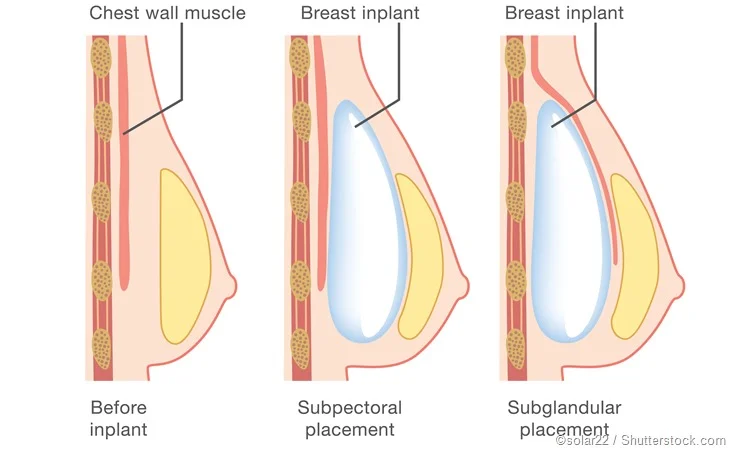
- 2. Implant Placement:
- Submuscular: Positioned beneath the chest muscles.
- Subglandular: Placed behind the breast tissue, over the chest muscles.
- Dual Plane: Combination of submuscular and subglandular placement.
- 3. Surgical Procedure:
- Preparation: Anesthesia administered; incision site and implant placement determined.
- Implant Placement: Implants inserted using chosen incision and placement technique.
- Closing Incisions: Incisions closed with sutures or surgical tape; dressings applied.
- 4. Recovery and Follow-up:
- Post-operative care involves monitoring healing, managing discomfort, and following specific instructions provided by the surgeon.
- Regular follow-up appointments to assess healing progress and address any concerns.
Choosing the appropriate implant type and surgical technique depends on factors like body type, desired results, and the surgeon’s recommendation. It’s essential to consult with a board-certified plastic surgeon to discuss options and create a personalized augmentation plan.
Breast Reduction: Alleviating Discomfort
Breast reduction surgery, aimed at alleviating discomfort associated with overly large breasts, addresses both physical and emotional concerns. Here’s an overview of its indications, techniques, and considerations regarding scarring:
Indications for Reduction Surgery:
- Physical Discomfort: Chronic neck, shoulder, or back pain due to the weight of large breasts.
- Posture Issues: Strain on the spine leading to poor posture or even skeletal deformities.
- Skin Irritation: Rashes, chafing, or irritation beneath the breasts due to skin-on-skin contact.
- Limitation in Physical Activity: Difficulty in participating in certain physical activities due to breast size.
Techniques and Scarring:
- 1. Surgical Approaches:
- Anchor or Inverted-T Technique: Most common method involving three incisions—around the areola, vertically down to the breast crease, and along the crease.
- Vertical or Lollipop Technique: Utilizes fewer incisions, omitting the horizontal incision along the breast crease, resulting in a lollipop-shaped scar.
- Liposuction-Assisted Breast Reduction: Suitable for cases with excess fatty tissue and minimal skin elasticity, involving smaller incisions and less scarring.
- 2. Scarring Considerations:
- Incision Lines: Scarring usually occurs around the areola, vertically down to the breast crease, and horizontally along the crease (if using the anchor technique).
- Scar Management: Surgeons provide guidance on scar care, including proper wound care, silicone sheets/gels, and scar massage to minimize their appearance.
- Scar Healing: Scars tend to fade over time, becoming less noticeable, but their visibility varies among individuals.
Post-Operative Recovery:
- Post-Surgery Support: Patients wear a surgical bra or compression garment to aid healing and reduce swelling.
- Pain Management: Medications prescribed to manage post-operative discomfort.
- Activity Restrictions: Advised to limit strenuous activities and follow specific post-operative care instructions provided by the surgeon.
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-ups to monitor healing and address any concerns.
Breast reduction surgery not only reduces breast size but also reshapes and lifts the breasts, aiming to improve overall comfort and confidence. While scarring is an inevitable aspect, proper post-operative care and adherence to the surgeon’s instructions can help minimize their appearance over time. Consulting with a qualified plastic surgeon is crucial to discuss individual goals, expectations, and the most suitable technique for achieving desired results.
Breast Lift (Mastopexy): Restoring Shape
A mastopexy, commonly known as a breast lift, is a surgical procedure designed to restore a more youthful and uplifted appearance to breasts that have lost volume, shape, or firmness due to factors like aging, pregnancy, weight fluctuations, or genetics. Here are insights into when a mastopexy might be necessary and considerations regarding mastopexy with or without implants:
When Is a Mastopexy Necessary?
- Sagging or Ptosis: Breasts lose firmness and begin to droop, often due to aging or post-pregnancy changes.
- Loss of Breast Volume: Breasts may appear deflated or elongated due to weight loss or breastfeeding.
- Nipple and Areola Position: Nipples might point downward or sit lower on the breast due to gravity or tissue laxity.
- Asymmetry: Addressing uneven or asymmetrical breasts to achieve balance and symmetry.
Mastopexy with or without Implants:
- Mastopexy Alone:
- Procedure Focus: Primarily focuses on lifting and reshaping existing breast tissue.
- Reshaping Technique: Involves repositioning and tightening breast tissue, removing excess skin, and elevating the breasts for a more youthful appearance.
- Ideal Candidates: Suitable for individuals satisfied with their breast volume but seeking a firmer and more uplifted position.
- Mastopexy with Implants (Augmentation-Mastopexy):
- Combination Approach: Involves lifting the breasts while simultaneously adding volume using implants.
- Enhanced Volume and Shape: Addresses both sagging and volume loss, providing a lifted appearance and increased breast size.
- Ideal Candidates: Suitable for individuals desiring both improved breast position and increased volume.
A mastopexy aims to restore a more youthful breast contour by reshaping existing breast tissue and repositioning the nipples for a more aesthetically pleasing appearance. Deciding whether to include implants alongside the lift depends on the desired outcome, and consulting with a qualified plastic surgeon is crucial in determining the most suitable approach for achieving desired results.
Breast Reconstruction: After Mastectomy
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy offers options to restore breast shape, symmetry, and self-confidence. Here are insights into the available reconstruction options and considerations regarding the timing of reconstruction:
Options for Breast Reconstruction:
- 1. Implant-Based Reconstruction:
- Using Implants: Involves inserting saline or silicone implants to reconstruct the breast mound.
- Staged Approach: Often requires tissue expanders placed initially to gradually stretch the skin before the final implant insertion.
- 2. Autologous or Flap Reconstruction:
- Tissue Flap Techniques: Utilizes tissue from the patient’s body (like abdomen, back, or thighs) to reconstruct the breast.
- Types of Flaps: Options include TRAM flap, DIEP flap, or latissimus dorsi flap, each with distinct donor site considerations.
- 3. Combined Approach:
- Hybrid Reconstruction: Combines implant-based techniques with autologous tissue to achieve desired volume and naturalness.
Timing of Reconstruction:
- Immediate Reconstruction:
- At the Time of Mastectomy: Reconstruction performed during the same surgery as the mastectomy.
- Advantages: Reduced number of surgeries, preserved skin for a more natural appearance, and psychological benefits of waking up with a reconstructed breast.
- Delayed Reconstruction:
- After Mastectomy Healing: Reconstruction performed at a later date following mastectomy.
- Advantages: Time for emotional adjustment, healing, or completion of additional cancer treatments before reconstruction.
- Factors Influencing Timing:
- Health Condition: Consideration of overall health and potential impact on recovery.
- Treatment Plan: Coordination with oncologists regarding radiation or chemotherapy treatments.
- Personal Preference: Individual comfort level and decision-making regarding immediate or delayed reconstruction.
- Expectations and Goals: Discussions with a plastic surgeon about desired outcomes and timing feasibility.
Considerations and Decision-Making:
- Consultation with a Plastic Surgeon: Essential to discuss individual options, risks, benefits, and expectations.
- Recovery Period: Understanding the recovery process and potential impact on lifestyle.
- Emotional Support: Accessing emotional support networks or counseling to navigate the emotional aspects of reconstruction.
Breast reconstruction is a highly personalized journey, and the choice of reconstruction type and timing depends on various factors, including individual preferences, medical considerations, and treatment plans. Open communication with healthcare providers helps in making informed decisions tailored to the individual’s needs and goals.
You may want to read about : Types of breast surgery for cancer in UAE
Gynecomastia Surgery: Male Breast Reduction
Gynecomastia refers to the enlargement of glandular tissue in the male breast, often leading to a more feminine contour. This condition can result from hormonal imbalances, certain medications, obesity, or genetic factors.
Understanding Gynecomastia:
- Tissue Enlargement: Gynecomastia involves the development of excess breast tissue, causing the appearance of larger breasts in males.
- Causes: Hormonal changes during puberty, imbalances in testosterone and estrogen levels, certain medications (such as steroids or some antidepressants), or medical conditions can contribute to gynecomastia.
- Effects: Apart from the physical appearance, gynecomastia might cause psychological discomfort, leading individuals to seek corrective measures.
Surgical Approaches for Male Patients:
- 1. Liposuction:
- Procedure: Utilizes a thin tube (cannula) to suction out excess fat from the breast area.
- Suitability: Effective for cases primarily involving excess fatty tissue rather than glandular enlargement.
- 2. Excision:
- Procedure: Involves surgical removal of excess glandular tissue and possibly skin through discreet incisions.
- Suitability: Effective for cases with substantial glandular tissue or excess skin, often combined with liposuction for optimal results.
- 3. Combination Approach:
- Liposuction and Excision: Surgeons may use a combination of liposuction and excision techniques to address both fatty tissue and glandular enlargement for comprehensive results.
- Tailored Approach: Customized to individual needs, ensuring a more masculine chest contour.
Considerations and Decision-Making:
- Consultation with a Plastic Surgeon: Crucial to assess the extent of gynecomastia, discuss goals, and determine the most suitable surgical approach.
- Realistic Expectations: Understanding achievable outcomes and limitations of the procedure.
- Recovery and Aftercare: Post-operative care instructions, recovery timeline, and temporary restrictions on activities.
- Potential Risks: Discussion about potential risks such as scarring, changes in nipple sensation, or asymmetry.
Gynecomastia surgery aims to achieve a more masculine chest contour by addressing the excess breast tissue or fatty deposits. The choice between liposuction, excision, or a combination thereof depends on the individual’s specific condition and desired outcomes. Consulting with a qualified plastic surgeon helps in determining the most appropriate approach for achieving optimal results.
Breast Asymmetry Correction
Breast asymmetry, where one breast differs in size, shape, or position from the other, is a common occurrence among many individuals. Here are insights into the causes and correction techniques for breast asymmetry:
Causes of Breast Asymmetry:
- 1. Developmental Factors:
- Puberty: Uneven breast development during adolescence.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations leading to differences in breast size or shape.
- 2. Congenital or Genetic Factors:
- Genetic Predisposition: Inherited traits that result in uneven breasts.
- Conditions: Congenital conditions affecting breast development.
- 3. Trauma or Surgery:
- Injuries or Surgeries: Trauma or previous surgeries that impact breast tissue differently.
- 4. Hormonal Changes or Weight Fluctuations:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Hormonal changes during pregnancy and breastfeeding can cause changes in breast size and shape.
- Weight Changes: Fluctuations in weight can affect breast size and symmetry.
Correction Techniques:
- 1. Breast Augmentation or Reduction:
- Augmentation: Implants used to increase size in smaller breasts to match the larger one.
- Reduction: Reducing the size of the larger breast to match the smaller one.
- 2. Mastopexy (Breast Lift):
- Surgical Lift: Lifting and reshaping the breast to achieve symmetry.
- Adjustment of Nipple and Areola: Repositioning nipples and areolas to match each other.
- 3. Combination Approaches:
- Augmentation with Lift: For cases requiring both volume adjustment and lift for symmetry.
- Reduction with Lift: Combining reduction techniques with a lift for balance.
- 4. Fat Transfer:
- Fat Grafting: Transferring fat from one area of the body to the smaller breast to achieve symmetry.
Considerations and Decision-Making:
- Consultation with a Plastic Surgeon: Essential to evaluate asymmetry, discuss options, and determine the best approach.
- Individual Goals: Understanding the desired outcomes and realistic expectations.
- Physical and Emotional Impact: Addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of asymmetry.
- Risks and Recovery: Being aware of potential risks, recovery process, and post-operative care instructions.
Correcting breast asymmetry involves various surgical techniques tailored to the individual’s specific condition and goals. Consulting with a qualified plastic surgeon helps in determining the most suitable approach for achieving improved symmetry and overall satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Procedure for You
Choosing the right procedure is a crucial decision that involves multiple factors. Here’s a breakdown of key considerations when selecting a procedure:
Consultation with a Qualified Surgeon:
- Expert Opinion: Seek guidance from a board-certified surgeon specializing in the desired procedure.
- Assessment: Surgeons evaluate your specific anatomy, medical history, and goals.
- Clarify Doubts: Ask questions about the procedure, risks, recovery, and expected outcomes.
- Review Options: Discuss different approaches available and their suitability for your case.
Considering Personal Goals and Expectations:
- Define Goals: Clearly articulate what you aim to achieve from the procedure.
- Realistic Expectations: Understand the achievable outcomes and limitations of the chosen procedure.
- Alignment with Lifestyle: Assess how the procedure aligns with your lifestyle, recovery time, and potential impact on daily activities.
- Address Concerns: Communicate any concerns or specific desires to the surgeon during consultation.
Additional Factors:
- Health Considerations: Consider your overall health and how it might affect the procedure and recovery.
- Financial Aspect: Evaluate costs, including procedure fees, follow-up visits, and any potential post-operative care expenses.
- Emotional Readiness: Acknowledge and prepare for the emotional impact of undergoing a surgical procedure.
Decision-Making Process:
- Research: Gather information about the procedure, its variations, and possible alternatives.
- Consultation: Meet with one or more qualified surgeons to discuss options, assess suitability, and gain insights.
- Personal Assessment: Reflect on the information provided during consultations and consider how each option aligns with your goals and expectations.
- Informed Decision: Make a decision based on a combination of professional guidance, personal preferences, and realistic expectations.
Choosing the right procedure involves a combination of medical expertise and personal considerations. Through open communication, thorough research, and careful consideration of personal goals, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your desires and leads to a successful outcome.
FAQs about Breast Surgery Procedures in UAE
1. What are the types of breast surgery procedures?
Breast surgery encompasses various procedures tailored to address different concerns:
- Breast Augmentation: Enhancing breast size using implants or fat transfer.
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy): Lifting and reshaping breasts for a more youthful contour.
- Breast Reduction: Reducing breast size to alleviate discomfort or achieve better proportions.
- Breast Reconstruction: Restoring breasts after mastectomy due to cancer or other medical reasons.
2. Which country is the best for breast surgery procedures?
The “best” country for breast surgery procedures can vary based on several factors, including:
- Expertise of Surgeons: Countries with highly skilled and experienced plastic surgeons.
- Regulatory Standards: Nations with stringent medical regulations ensuring safety and quality.
- Personal Preferences: Consideration of travel, costs, and post-operative care.
The UAE, with its advanced medical facilities and skilled practitioners, is known to offer quality breast surgery procedures. However, individual preferences and needs should guide the choice of location.
3. What is the most common breast procedure?
The most common breast procedure varies based on factors such as regional trends, patient preferences, and medical needs. Generally, breast augmentation (enlargement) tends to be among the most frequently performed procedures globally. However, breast procedures like lifts (mastopexy) and reductions are also commonly sought for addressing sagging or discomfort.
In the UAE, breast augmentation, aimed at enhancing breast size, is frequently requested, followed by breast lifts and reconstructions.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon to determine the most suitable procedure based on individual goals and anatomical considerations.




Leave a Reply