Hepatitis C is a viral infection that targets the liver, causing inflammation and potentially leading to serious liver damage. It spreads through exposure to infected blood, often through sharing needles or unsafe medical procedures. Many people with Hepatitis C don’t exhibit symptoms immediately, which can delay diagnosis.
Understanding Hepatitis C
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver, causing inflammation. It’s transmitted through blood-to-blood contact, often due to sharing needles or through blood transfusions. In some cases, it can also spread through sexual contact.
Types of Hepatitis C Infections
There are different genotypes of the Hepatitis C virus, each with its own variations. Genotypes 1, 2, and 3 are the most common, and their treatment approaches might vary.
Global Impact and Prevalence
Hepatitis C is a significant global health issue. It’s estimated that millions of people are affected worldwide. The prevalence varies across regions, with certain areas having higher rates due to specific risk factors and healthcare access.
Understanding the nature of Hepatitis C, its different forms, and its prevalence globally is crucial in addressing and managing this health concern
Transmission and Risk Factors
How is Hepatitis C Transmitted?
Hepatitis C is primarily transmitted through blood-to-blood contact. Common modes of transmission include:
- Sharing Needles: Sharing needles or syringes, especially among people who inject drugs, is a significant risk factor.
- Blood Transfusions: While rare today due to improved blood screening, Hepatitis C used to be transmitted through blood transfusions and organ transplants before screening measures were widespread.
- Needlestick Injuries: Healthcare workers can be at risk if they experience accidental needlestick injuries involving infected blood.
- Mother-to-Child Transmission: While less common, a pregnant woman with Hepatitis C can pass the virus to her baby during childbirth.
Who is at Risk for Hepatitis C?
Certain groups are at a higher risk of contracting Hepatitis C:
- People Who Inject Drugs: This group has a higher likelihood of exposure due to needle sharing.
- Healthcare Workers: Those who handle needles or come into contact with infected blood are at risk of accidental exposure.
- People Who Received Blood Products Before Screening: Before blood screening became standard, those who received blood transfusions or organ transplants were at higher risk.
- Infants Born to Infected Mothers: While the risk is relatively low, infants born to mothers with Hepatitis C have a chance of contracting the virus during childbirth.
Needlestick and Bloodborne Exposure
Healthcare workers, including nurses, doctors, and lab technicians, are at risk of Hepatitis C through accidental needlestick injuries or exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. Proper safety protocols, including the use of safety needles and adherence to universal precautions, are crucial in minimizing these risks in healthcare settings. Prompt reporting and access to post-exposure prophylaxis can also mitigate the risk of infection following exposure.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
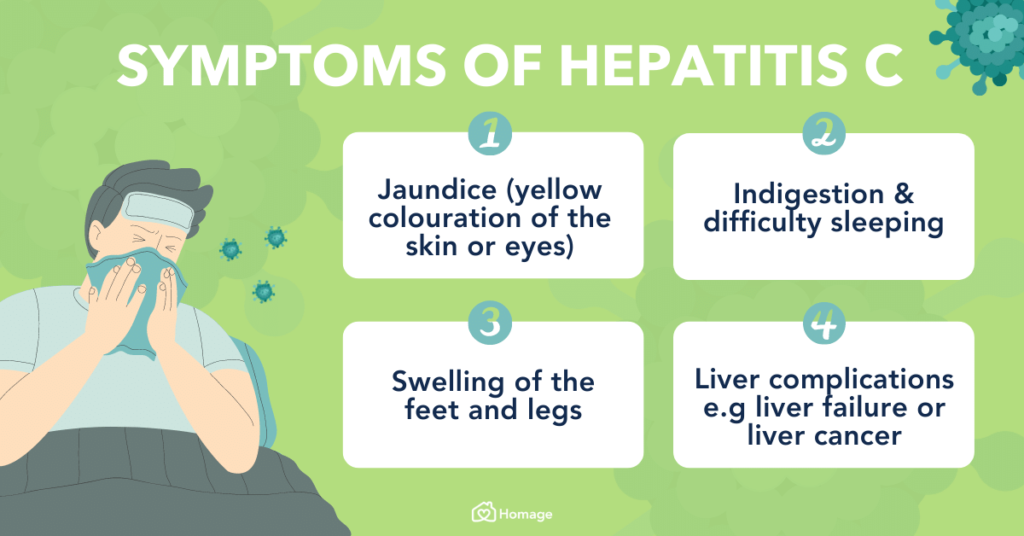
Common Symptoms of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C often progresses silently without noticeable symptoms for years. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Joint pain
- Dark urine
- Pale-colored stools
- Tenderness in the liver area
Hepatitis C Testing and Diagnosis
Testing for Hepatitis C involves blood tests that check for the presence of antibodies to the virus or the virus itself. Common tests include:
- HCV Antibody Test: Detects antibodies the body produces in response to the Hepatitis C virus.
- HCV RNA Test: Detects the genetic material of the virus in the blood, confirming an active infection.
Stages of Hepatitis C Infection
Hepatitis C infection progresses through several stages:
- Acute Hepatitis C: This occurs within the first six months after exposure. Most people don’t show symptoms during this phase, but some might experience mild illness.
- Chronic Hepatitis C: When the virus persists in the body beyond six months, it becomes chronic. This stage often remains asymptomatic for years but can lead to liver damage over time.
- Cirrhosis: Long-term infection can lead to liver scarring or cirrhosis, which can cause serious complications, including liver failure or liver cancer in some cases.
Early diagnosis through testing is crucial in managing Hep C effectively. Treatment during the acute phase can prevent chronic infection, and managing chronic Hepatitis C can prevent or slow down liver damage. Regular monitoring helps track the progression and guides treatment decisions.
You may want to read: Unmasking Hepatitis B in the UAE (Prevalence and Prevention)
Treatment Options for Hepatitis C
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral drugs are the primary treatment for Hep C. They aim to clear the virus from the body and prevent liver damage. Common medications include:
- Direct-Acting Antivirals (DAAs): These drugs target specific steps in the virus’s lifecycle, inhibiting its replication. DAAs are highly effective and have fewer side effects compared to older treatments.
- Combination Therapies: Sometimes, several antiviral drugs are used in combination to increase effectiveness and prevent the development of drug-resistant strains.
New Advances in Hepatitis C Treatment
Advancements in Hep C treatment have significantly improved cure rates and reduced treatment duration. Some notable advances include:
- High Cure Rates: DAAs have shown cure rates exceeding 95% in many cases, even for previously difficult-to-treat genotypes.
- Shortened Treatment Duration: Treatment durations have significantly shortened, often to 8-12 weeks, depending on the specific medication and the patient’s condition.
- Fewer Side Effects: Newer medications have fewer side effects compared to older interferon-based treatments, leading to better tolerance and adherence to treatment regimens.
Monitoring and Management
After initiating treatment, monitoring is essential to assess the response to therapy and ensure optimal outcomes:
- Follow-Up Testing: Regular blood tests during and after treatment help monitor viral levels to confirm successful eradication of the virus.
- Liver Health Management: Managing other aspects that can affect liver health, such as alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting vaccinated against Hepatitis A and B, is crucial.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Even after successful treatment and viral clearance, regular check-ups are recommended to monitor liver health and detect any signs of recurrence.
The advancements in Hepatitis C treatment have transformed the landscape, offering highly effective and tolerable therapies. Early diagnosis, access to treatment, and consistent monitoring significantly improve outcomes for individuals with Heps C.
Prevention and Screening
Hepatitis C Prevention Strategies
Preventing Hepatitis C transmission involves various strategies:
- Avoid Sharing Needles: Encourage needle exchange programs and provide education on safe injection practices to minimize the risk among individuals who inject drugs.
- Practice Safe Sex: While the risk is lower compared to other modes of transmission, using condoms can reduce the risk of sexual transmission.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Items like razors or toothbrushes that might have blood on them should not be shared.
- Ensure Safe Healthcare Practices: Sterilize medical equipment properly and use precautions to prevent exposure to infected blood in healthcare settings.
Importance of Screening and Testing
Screening for Hepatitis C is crucial for several reasons:
- Early Detection: Many people with Hepatitis C are asymptomatic. Screening helps identify infections early, allowing for timely treatment and preventing long-term complications.
- Preventing Transmission: Identifying infected individuals helps prevent the spread of the virus to others through targeted interventions.
- Improving Outcomes: Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve treatment success rates and reduce the risk of liver damage.
Preventing Transmission in Healthcare Settings
Healthcare settings need robust measures to prevent Hep C transmission:
- Universal Precautions: Adhering to strict infection control practices, including using gloves, masks, and proper disposal of needles, helps minimize the risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
- Safe Needle Practices: Implementing safety-engineered devices and proper needle disposal procedures can reduce the risk of needlestick injuries among healthcare workers.
- Training and Education: Providing comprehensive training on infection control practices and ensuring healthcare workers are aware of protocols for handling blood and bodily fluids is essential.
Prevention, early detection through screening, and strict adherence to safety protocols in healthcare settings are pivotal in reducing the burden of Hepatitis C and preventing new infections.
Living with Hepatitis C
Managing Chronic Hepatitis C
Living with chronic Hepatitis C involves:
- Medical Management: Follow the prescribed treatment plan, attend regular check-ups, and take medications as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy diet, avoid alcohol and substances that can harm the liver, and exercise regularly to support overall health.
- Regular Monitoring: Continual monitoring of liver health is important even after successful treatment to detect any potential complications.
Disclosure and Relationships
Deciding to disclose a Hepatitis C diagnosis and managing relationships can be sensitive:
- Disclosure: It’s a personal choice whether or not to disclose your diagnosis. Educating close contacts about transmission routes and preventive measures can help reduce concerns.
- Intimate Relationships: While the risk of sexual transmission is low, it’s advisable to use precautions like condoms to further minimize the risk.
Supportive Care and Coping Strategies
Coping with Hepatitis C can be challenging, but there are ways to manage it:
- Support Groups: Joining support groups or seeking counseling can provide emotional support and practical advice from others going through similar experiences.
- Education: Educate yourself about Hepatitis C to better understand the condition and actively participate in your treatment and care decisions.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-relief techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or hobbies to reduce stress, which can positively impact overall health.
Living with Hep C involves a multidimensional approach—managing health, relationships, and emotional well-being. Engaging with support systems, staying informed, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can enhance the quality of life while managing the condition.
Support and Resources
here are some resources and avenues for support, medical guidance, and educational materials related to Hepatitis C:
Hepatitis C Support Groups
- Hepatitis C Alliance: Offers support groups, information, and resources for individuals and families affected by Hepatitis C.
- American Liver Foundation: Provides support services, community forums, and educational materials for individuals living with liver diseases, including Hepatitis C.
- Local Health Centers: Many local health centers and hospitals offer support groups specifically for individuals dealing with Hepatitis C. Check with your healthcare provider or community health services for local options.
Medical Specialists and Hepatitis C Clinics
- Hepatologists: These specialists focus on liver diseases and are well-equipped to manage Hepatitis C cases.
- Infectious Disease Specialists: Some infectious disease specialists have expertise in treating Hepatitis C.
- Hepatitis C Clinics: Specialized clinics dedicated to Hepatitis C management might be available in larger healthcare centers or academic institutions. These clinics often offer comprehensive care, including access to clinical trials and the latest treatment options.
Educational Materials and Websites
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC website offers extensive resources, educational materials, and guidelines on Hepatitis C for both healthcare professionals and the general public.
- Hepatitis C Online: This website provides a wealth of information, including clinical resources, training modules, and patient education materials.
- Hepatitis C Support Project: Offers educational materials, treatment information, and resources for individuals navigating Hepatitis C diagnosis and treatment.
These resources can offer valuable support, information, and connections to specialized healthcare providers for individuals living with Hep C and their families. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans.
FAQs:
How is Hep C treated in UAE?
Hepatitis C treatment in the UAE follows global standards and often includes direct-acting antiviral medications (DAAs) that target the virus, aiming for its eradication. The UAE healthcare system provides access to these effective antiviral treatments, allowing individuals to undergo therapy under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
Is hepatitis common in UAE?
Hepatitis, including Hepatitis C, is present in the UAE, but the prevalence might vary. The UAE, like many other countries, has implemented measures to control and manage hepatitis infections, including raising awareness, offering vaccinations, and providing access to treatments to reduce the incidence and impact of these infections.
Can you have a normal life with Hep C?
Yes, with appropriate treatment and management, many people with Hep C can lead normal lives. Successful treatment can clear the virus from the body, reducing the risk of liver damage. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, regular check-ups, and avoiding alcohol and liver-damaging substances can help maintain liver health.
Can Hep C be cured forever?
Yes, Hepatitis C can be cured. Modern treatments, such as direct-acting antiviral medications (DAAs), have shown high cure rates, often exceeding 95%. Successful treatment can result in the complete eradication of the virus from the body, leading to a cure.
Is Hep C completely cured?
Yes, successful treatment with modern antiviral medications can result in a complete cure for Hep C. However, it’s essential to continue monitoring liver health periodically even after successful treatment to ensure there is no recurrence of the virus or development of liver-related complications.
Treatment advancements have significantly improved the outlook for individuals with Hep C, with high cure rates achievable and the possibility of leading a healthy, normal life post-treatment. Regular monitoring and adherence to healthcare advice are crucial for long-term health and well-being.




Leave a Reply