Hepatitis B in UAE is a critical health concern worldwide, including in Abu Dhabi. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the essential aspects of Hepatitis B, including its causes, transmission, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention methods, and the impact of Hepatitis B on various aspects of life, including pregnancy.
Additionally, we will address frequently asked questions related to Hepatitis B and its implications on employment and travel. By understanding Hepatitis B and its associated guidelines, individuals in Abu Dhabi can make informed decisions to protect their health and well-being.
Understanding Hepatitis B in UAE
What is Hepatitis B?
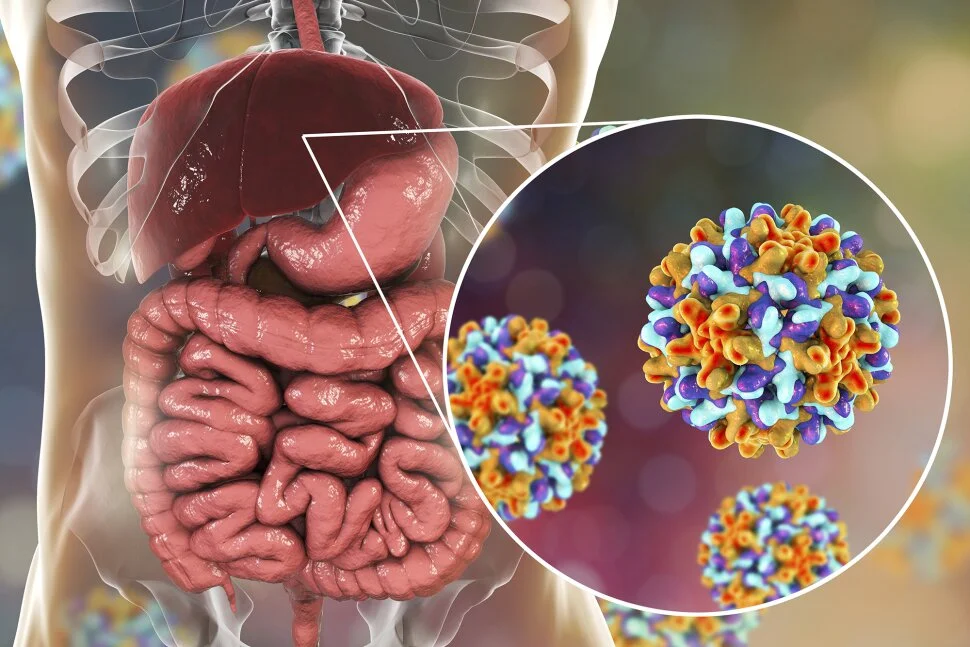
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause serious health problems, including liver failure, cirrhosis, and cancer. The virus is transmitted through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids, such as semen and vaginal fluids.
Types of Hepatitis B Infections
There are two main types of hepatitis B infections: acute and chronic.
- Acute hepatitis B is a short-term infection that usually goes away on its own within a few months.
- Chronic hepatitis B is a long-term infection that can last for years or even decades. Chronic hepatitis B can lead to serious health problems, such as liver failure, cirrhosis, and cancer.
Hepatitis B Causes and Transmission
How is Hepatitis B Transmitted?
Hepatitis B is transmitted through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids, such as semen and vaginal fluids. The virus can be spread through:
- Sexual contact with an infected person
- Sharing needles or syringes with an infected person
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant from an infected person
- Being born to an infected mother
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unsterilized equipment
At-Risk Groups for Hepatitis B
Certain people are at higher risk for hepatitis B infection, including:
- People who have unprotected sex with multiple partners
- People who inject drugs
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B
- People who work in healthcare or public safety professions
- People who travel to countries where hepatitis B is common
- People who were born in or have parents from countries where hepatitis B is common
Symptoms and Signs of Hepatitis B
Common Symptoms of Hepatitis B
The symptoms of hepatitis B can vary depending on the type of infection. People with acute hepatitis B may experience the following symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark-colored urine
- Light-colored stools
People with chronic hepatitis B may not experience any symptoms for many years. However, some people may develop the following symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Jaundice
- Dark-colored urine
- Light-colored stools
- Swelling in the legs and feet
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the symptoms of hepatitis B, it is important to see a doctor right away. Hepatitis B can be a serious condition, and early diagnosis and treatment are essential.
Read also COVID-19 Guidelines Abu Dhabi: 5 Steps to Safeguard Your Health
Hepatitis B Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnostic Tests for Hepatitis B
To diagnose hepatitis B, a doctor will typically order a blood test to look for the hepatitis B virus. The doctor may also order other tests, such as an ultrasound or liver biopsy, to assess the damage to the liver.
Interpreting Hepatitis B Test Results
The following are the most common hepatitis B tests and their results:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg): A positive HBsAg test means that you are currently infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- Hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg): A positive HBeAg test means that you are highly contagious.
- Hepatitis B core antibody (HBcAb): A positive HBcAb test means that you have been infected with the hepatitis B virus in the past.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb): A positive HBsAb test means that you are immune to the hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B Treatment Options
Medications for Hepatitis B
There is no cure for hepatitis B, but there are medications that can help to control the virus and prevent it from damaging the liver. Medications for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral drugs: Antiviral drugs can help to suppress the hepatitis B virus and reduce the risk of liver damage.
- Interferon: Interferon is a protein that helps the body to fight off infection. Interferon can be used to treat chronic hepatitis B in some cases.
Lifestyle Changes and Management
In addition to medication, there are a number of lifestyle changes that people with hepatitis B can make to manage their condition, including:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Avoiding alcohol and tobacco
- Getting vaccinated against other liver infections, such as hepatitis A and hepatitis C
Preventing Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Vaccination
The hepatitis B vaccine is the best way to prevent hepatitis B infection. The vaccine is safe and effective, and it is recommended for all infants, children, and adults. The vaccine is given in a series of three shots.
Safe Practices to Prevent Infection
In addition to vaccination, there are a number of safe practices that can help to prevent hepatitis B infection, including:
- Using condoms during sexual intercourse
- Not sharing needles or syringes
- Getting tattoos and piercings with sterile equipment
- Avoiding contact with the blood and bodily fluids of infected people
Living with Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to see a doctor regularly to monitor your condition and manage your symptoms. There are a number of things you can do to live a healthy life with hepatitis B, including:
Diet and Nutrition Tips
Eating a healthy diet is important for everyone, but it is especially important for people with hepatitis B. A healthy diet can help to reduce the risk of liver damage and improve overall health.
Here are some tips for eating a healthy diet with hepatitis B:
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables
- Choose whole grains over refined grains
- Choose lean protein sources, such as chicken, fish, and beans
- Limit saturated and unhealthy fats
- Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks
Mental and Emotional Well-being
Living with a chronic illness can be challenging, and it is important to take care of your mental and emotional well-being. There are a number of things you can do to support your mental and emotional health, including:
- Talking to a therapist or counselor
- Joining a support group for people with hepatitis B
- Practicing stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation
- Getting regular exercise
Hepatitis B Vaccination
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all infants, children, and adults. It is especially important for people who are at high risk for hepatitis B infection, such as:
- People who have unprotected sex with multiple partners
- People who inject drugs
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B
- People who work in healthcare or public safety professions
- People who travel to countries where hepatitis B is common
- People who were born in or have parents from countries where hepatitis B is common
Vaccination Schedule and Booster Shots
The hepatitis B vaccine is given in a series of three shots. The first two shots are given one month apart, and the third shot is given six months after the first shot.
A booster shot is recommended for adults who are at high risk for hepatitis B infection. The booster shot is given 10 years after the third shot.
Hepatitis B and Pregnancy
Transmission Risks to Newborns
Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies during childbirth. However, there are things that can be done to reduce the risk of transmission, such as giving the baby the hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours of birth.
Managing Hepatitis B during Pregnancy
Pregnant women with hepatitis B should work with their doctor to manage their condition and reduce the risk of transmission to their babies. This may include taking antiviral medications and getting regular blood tests to monitor the virus.
Support and Resources for Hepatitis B Patients in UAE
Patient Support Groups
There are a number of patient support groups available for people with hepatitis B. These groups can provide support and information to people who are living with the condition.
Where to Find Reliable Information
There are a number of reliable sources of information about hepatitis B. Some good places to start include:
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- The World Health Organization (WHO)
- The Hepatitis B Foundation
FAQs about hepatitis B In UAE
Can I work in Abu Dhabi if I have hepatitis B?
It depends on your job. There are some jobs in Abu Dhabi that are restricted to people who are free of hepatitis B, such as jobs in healthcare, food service, and education. However, there are also many jobs that you can work in Abu Dhabi if you have hepatitis B, such as jobs in business, technology, and tourism.

If you are unsure whether or not you will be able to work in Abu Dhabi with hepatitis B, you should contact the Abu Dhabi Health Authority (HAAD) for more information.
Is hepatitis B common in the UAE?
Hepatitis B is not as common in the UAE as it is in some other countries, but it is still present. The prevalence of hepatitis B in the UAE is estimated to be around 1%.
What is the rate of Hep B in UAE?
The prevalence of hepatitis B in the UAE is estimated to be around 1%. This means that about 1 in 100 people in the UAE have hepatitis B.
Can I get a US visa if I have hepatitis B?
Yes, you can get a US visa if you have hepatitis B. However, you may need to provide additional documentation, such as a medical certificate from a doctor.




1 Comment