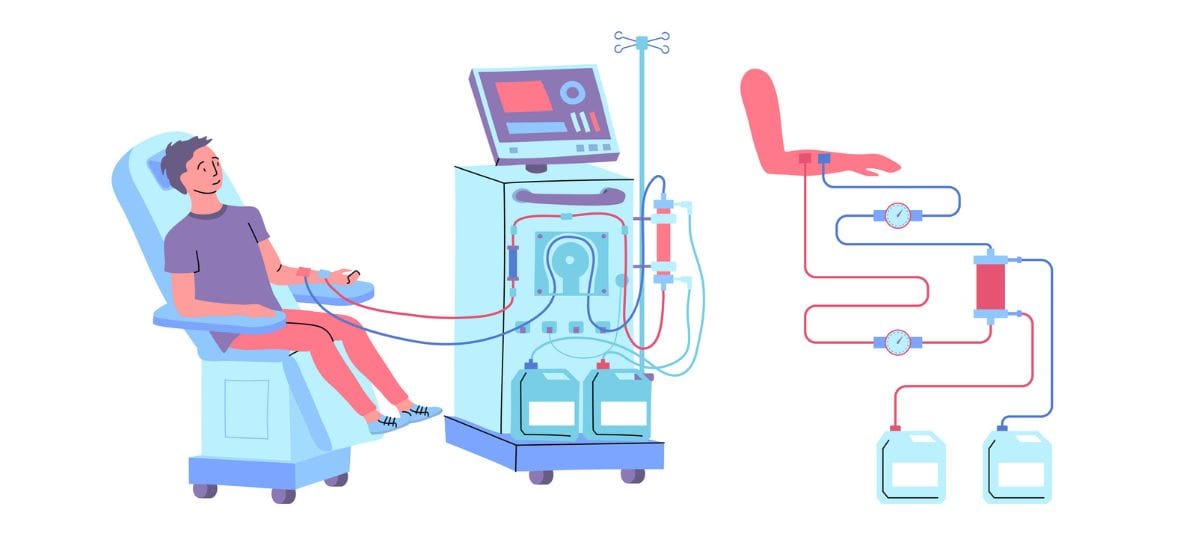
Overview Of Dialysis
Dialysis is a medical treatment that helps remove waste, toxins, and excess fluid from the body when the kidneys are unable to perform their natural function. It is commonly used for individuals with kidney failure or severe kidney damage. Dialysis can be performed through two main methods: hemodialysis, where blood is filtered through a machine, and peritoneal dialysis, where the lining of the abdomen filters waste. Dialysis is typically required when kidney function drops to 15% or less of its normal capacity.
Symptoms of Dialysis
- Patients who need dialysis often experience symptoms of kidney failure, such as fatigue, swelling, shortness of breath, nausea, and difficulty urinating. In some cases, symptoms may worsen as kidney function continues to decline, and the body accumulates waste products and fluid. Dialysis helps alleviate these symptoms by performing the kidney's job of filtering the blood.
Causes of Dialysis
- Dialysis is required when the kidneys lose their ability to filter blood effectively, which can be caused by conditions such as chronic kidney disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or kidney infections. These conditions damage the kidneys over time, leading to a decline in kidney function. Once kidney function reaches a critical point, dialysis becomes necessary to maintain proper waste removal and fluid balance in the body.
Risk Factors of Dialysis
- Risk factors for needing dialysis include diabetes, high blood pressure, a family history of kidney disease, and older age. Other factors that can increase the likelihood of kidney failure and the need for dialysis include obesity, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle. Early detection and management of underlying health conditions can help prevent the progression to kidney failure.
Prevention of Dialysis
- Preventing the need for dialysis involves managing the underlying causes of kidney damage, such as controlling diabetes, maintaining healthy blood pressure, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle. Early detection and treatment of kidney disease can slow its progression and delay or prevent the need for dialysis.
Prognosis of Dialysis
- The prognosis for individuals on dialysis depends on factors such as the underlying cause of kidney failure, overall health, and the type of dialysis used. While dialysis can help manage symptoms and prolong life, it is not a cure for kidney failure. Some patients may eventually undergo a kidney transplant, which offers a better long-term outcome.
Complications of Dialysis
- Potential complications of dialysis include infections, blood clots, low blood pressure, and electrolyte imbalances. For hemodialysis, there is also a risk of problems related to the vascular access site, while peritoneal dialysis carries risks of peritonitis (infection of the abdominal lining). Regular monitoring and proper care can help minimize these risks.
Related Diseases of Dialysis
- Kidney diseases that can lead to dialysis include chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetic nephropathy, hypertension-related kidney damage, and glomerulonephritis. Dialysis is also used for acute kidney failure, which may result from a sudden injury or illness. In these cases, dialysis may be temporary, but chronic conditions often require long-term dialysis.
Treatment of Dialysis
Dialysis is the primary treatment for kidney failure and is performed either through hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis involves the use of a machine to filter the blood, while peritoneal dialysis involves using the abdomen's lining as a natural filter. The type of dialysis chosen depends on the patient's medical condition, preferences, and available resources. Dialysis is usually performed several times a week, depending on the severity of kidney failure.
Generics For Dialysis
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Acetic Acid .469% + Calcium Chloride 1.008% + Magnessium Chloride .754% + Potassium Chloride .554% + Sodium Chloride 21.968%
Acetic Acid .469% + Calcium Chloride 1.008% + Magnessium Chloride .754% + Potassium Chloride .554% + Sodium Chloride 21.968%

Calcium Chloride .514 % + Magnessium Chloride .356 + Potassium Chloride .521 % + Sodium Acetate 18.088 % + Sodium Chloride 19.84 % (Hemodialysis solutions)
Calcium Chloride .514 % + Magnessium Chloride .356 + Potassium Chloride .521 % + Sodium Acetate 18.088 % + Sodium Chloride 19.84 % (Hemodialysis solutions)

Calcium Chloride + Dextrose Anhydrous + Magnessium Chloride + Sodium Acetate + Sodium Chloride (Peritoneal Dialysis solutions)
Calcium Chloride + Dextrose Anhydrous + Magnessium Chloride + Sodium Acetate + Sodium Chloride (Peritoneal Dialysis solutions)

Calcium Chloride + Glacial Acetic Acid + Magnessium Chloride + Potassium Chloride + Sodium Chloride (Hemodialysis solutions)
Calcium Chloride + Glacial Acetic Acid + Magnessium Chloride + Potassium Chloride + Sodium Chloride (Hemodialysis solutions)

Folic Acid + Vitamin B6 + Vitamin B12
Folic Acid + Vitamin B6 + Vitamin B12

Sodium Bicarbonate 6.6% + Sodium Chloride 3.1% + Highly purified water (Haemodialysis solutions)
Sodium Bicarbonate 6.6% + Sodium Chloride 3.1% + Highly purified water (Haemodialysis solutions)

Dextrose Hydrous + Sodium Chloride + Sodium Lactate + Calcium chloride + Magnesium chloride (Peritoneal dialysis solution)
Dextrose Hydrous + Sodium Chloride + Sodium Lactate + Calcium chloride + Magnesium chloride (Peritoneal dialysis solution)

Sodium Chloride + Sodium Lactate + Calcium chloride + Magnesium chloride (CAPD solutions)
Sodium Chloride + Sodium Lactate + Calcium chloride + Magnesium chloride (CAPD solutions)

Acetic Acid .469% + Calcium Chloride 1.008% + Magnessium Chloride .754% + Potassium Chloride .554% + Sodium Chloride 21.968%
Acetic Acid .469% + Calcium Chloride 1.008% + Magnessium Chloride .754% + Potassium Chloride .554% + Sodium Chloride 21.968%

Calcium Chloride .514 % + Magnessium Chloride .356 + Potassium Chloride .521 % + Sodium Acetate 18.088 % + Sodium Chloride 19.84 % (Hemodialysis solutions)
Calcium Chloride .514 % + Magnessium Chloride .356 + Potassium Chloride .521 % + Sodium Acetate 18.088 % + Sodium Chloride 19.84 % (Hemodialysis solutions)

Calcium Chloride + Dextrose Anhydrous + Magnessium Chloride + Sodium Acetate + Sodium Chloride (Peritoneal Dialysis solutions)
Calcium Chloride + Dextrose Anhydrous + Magnessium Chloride + Sodium Acetate + Sodium Chloride (Peritoneal Dialysis solutions)

Calcium Chloride + Glacial Acetic Acid + Magnessium Chloride + Potassium Chloride + Sodium Chloride (Hemodialysis solutions)
Calcium Chloride + Glacial Acetic Acid + Magnessium Chloride + Potassium Chloride + Sodium Chloride (Hemodialysis solutions)

Folic Acid + Vitamin B6 + Vitamin B12
Folic Acid + Vitamin B6 + Vitamin B12

Sodium Bicarbonate 6.6% + Sodium Chloride 3.1% + Highly purified water (Haemodialysis solutions)
Sodium Bicarbonate 6.6% + Sodium Chloride 3.1% + Highly purified water (Haemodialysis solutions)

Dextrose Hydrous + Sodium Chloride + Sodium Lactate + Calcium chloride + Magnesium chloride (Peritoneal dialysis solution)
Dextrose Hydrous + Sodium Chloride + Sodium Lactate + Calcium chloride + Magnesium chloride (Peritoneal dialysis solution)

Sodium Chloride + Sodium Lactate + Calcium chloride + Magnesium chloride (CAPD solutions)
Sodium Chloride + Sodium Lactate + Calcium chloride + Magnesium chloride (CAPD solutions)