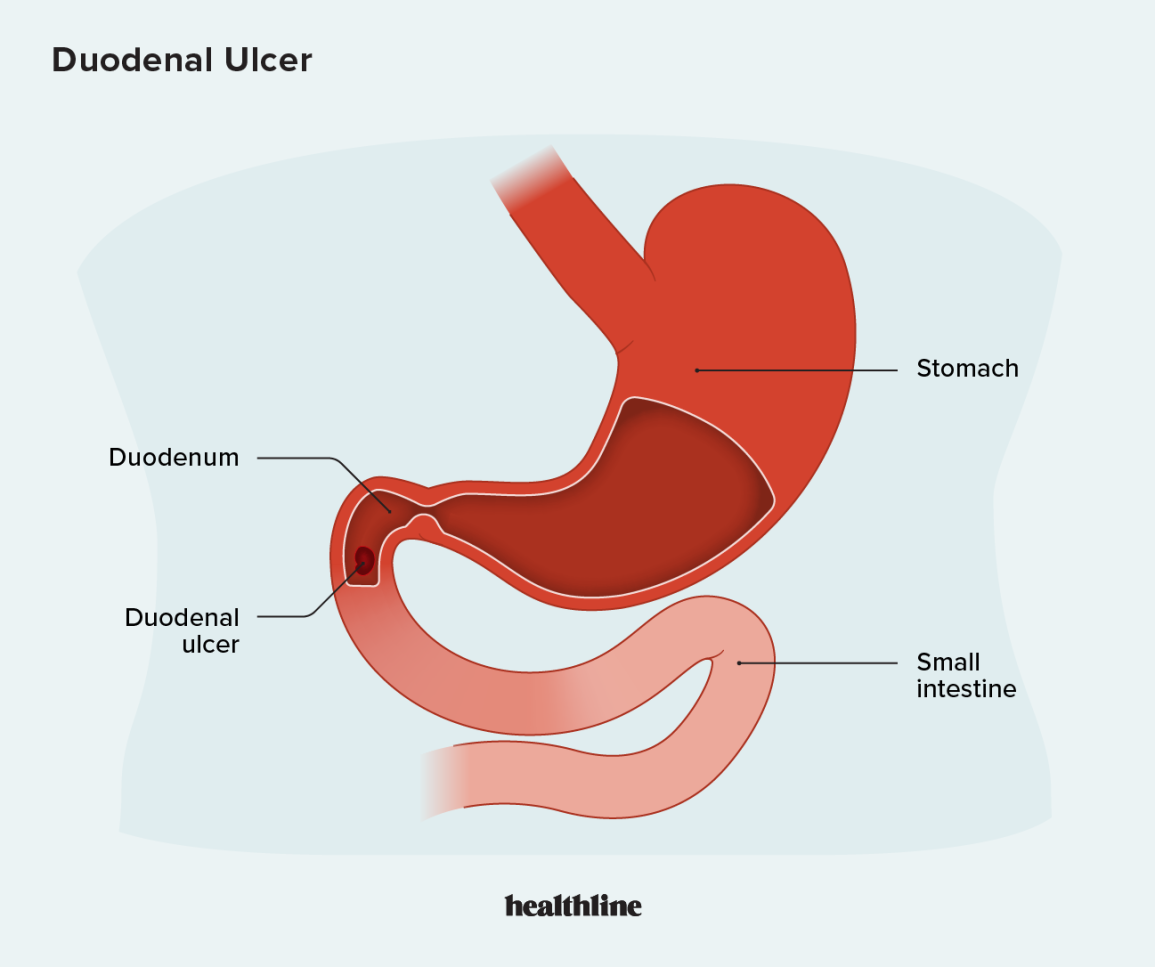
Overview Of Duodenal ulcer
Duodenal ulcers are open sores that develop on the inner lining of the duodenum. They are a form of peptic ulcer disease, which also includes gastric ulcers occurring in the stomach.
Symptoms of Duodenal ulcer
- Common symptoms of duodenal ulcers include: - A burning or gnawing pain in the stomach area, typically occurring between meals or at night. - Bloating and abdominal fullness. - Nausea or vomiting. - Loss of appetite and weight loss.
Causes of Duodenal ulcer
- The primary causes of duodenal ulcers include: - Infection with *Helicobacter pylori* (*H. pylori*) bacteria, which damages the protective mucous lining of the duodenum. - Long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen, which can harm the mucous lining.
Risk Factors of Duodenal ulcer
- Factors that increase the risk of developing duodenal ulcers include: - Smoking, which can increase stomach acid production and hinder healing. - Excessive alcohol consumption, which can irritate and erode the mucous lining. - Stress and spicy foods, though they do not cause ulcers, can exacerbate symptoms.
Prevention of Duodenal ulcer
- Preventive measures involve: - Avoiding long-term use of NSAIDs. - Limiting alcohol intake. - Quitting smoking. - Practicing good hygiene to prevent *H. pylori* infection.
Prognosis of Duodenal ulcer
- With appropriate treatment, most duodenal ulcers heal without complications. However, if left untreated, they can lead to serious health issues.
Complications of Duodenal ulcer
- Potential complications include: - Internal bleeding, which can cause anemia. - Perforation, leading to peritonitis, a severe abdominal infection. - Scar tissue formation causing obstruction in the digestive tract.
Related Diseases of Duodenal ulcer
- Conditions related to duodenal ulcers include: - Gastric ulcers. - Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). - Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. For more detailed information, please refer to the Mayo Clinic's page on peptic ulcers.
Treatment of Duodenal ulcer
Treatment options encompass: - Antibiotics to eradicate *H. pylori* infection. - Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce stomach acid production. - Antacids to neutralize existing stomach acid. - Discontinuation or substitution of NSAIDs with alternative pain relievers.
Generics For Duodenal ulcer
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Esomeprazole Sodium Injection
Esomeprazole Sodium Injection

Omeprazole + Metronidazole + Clarithromycin
Omeprazole + Metronidazole + Clarithromycin

Omeprazole
Omeprazole

Aluminium Hydroxide
Aluminium Hydroxide

Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Hydroxide
Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Hydroxide

Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Trisilicate
Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Trisilicate

Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Hydroxide
Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Hydroxide

Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Trisilicate
Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Trisilicate

Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Lansoprazole Kit
Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Lansoprazole Kit

Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Rabeprazole Sodium kit
Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Rabeprazole Sodium kit

Cimetidine
Cimetidine

Clarithromycin + Metronidazole + Lansoprazol
Clarithromycin + Metronidazole + Lansoprazol

Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate BP
Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate BP

Famotidine
Famotidine

Lansoprazole
Lansoprazole

Magaldrate + Simethicone
Magaldrate + Simethicone

Magaldrate + Simethicone Chewable
Magaldrate + Simethicone Chewable

Misoprostol
Misoprostol

Nizatidine
Nizatidine

Omeprazole 20mg + Sodium bicarbonate 1100mg
Omeprazole 20mg + Sodium bicarbonate 1100mg

Rabeprazole
Rabeprazole

Roxatidine
Roxatidine

Sucralfate
Sucralfate

Esomeprazole Sodium Injection
Esomeprazole Sodium Injection

Omeprazole + Metronidazole + Clarithromycin
Omeprazole + Metronidazole + Clarithromycin

Omeprazole
Omeprazole

Aluminium Hydroxide
Aluminium Hydroxide

Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Hydroxide
Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Hydroxide

Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Trisilicate
Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Trisilicate

Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Hydroxide
Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Hydroxide

Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Trisilicate
Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Trisilicate

Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Lansoprazole Kit
Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Lansoprazole Kit

Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Rabeprazole Sodium kit
Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Rabeprazole Sodium kit

Cimetidine
Cimetidine

Clarithromycin + Metronidazole + Lansoprazol
Clarithromycin + Metronidazole + Lansoprazol

Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate BP
Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate BP

Famotidine
Famotidine

Lansoprazole
Lansoprazole

Magaldrate + Simethicone
Magaldrate + Simethicone

Magaldrate + Simethicone Chewable
Magaldrate + Simethicone Chewable

Misoprostol
Misoprostol

Nizatidine
Nizatidine

Omeprazole 20mg + Sodium bicarbonate 1100mg
Omeprazole 20mg + Sodium bicarbonate 1100mg

Rabeprazole
Rabeprazole

Roxatidine
Roxatidine

Sucralfate
Sucralfate