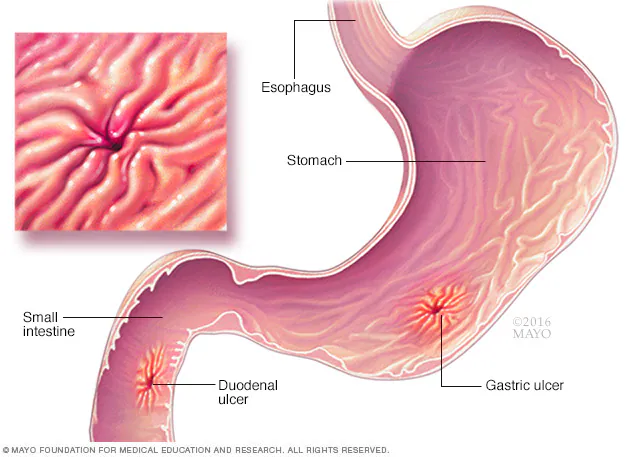
Overview Of Gastric ulcer
A gastric ulcer is an open sore that develops on the inner lining of the stomach. These ulcers occur when the stomach's protective mucus layer is compromised, allowing stomach acid to damage the underlying tissue. The most common symptom of a gastric ulcer is stomach pain.
Symptoms of Gastric ulcer
- - Burning or gnawing stomach pain, often occurring when the stomach is empty. - Bloating. - Indigestion. - Nausea or vomiting. - Loss of appetite. - In severe cases, vomiting blood or passing black stools, indicating potential bleeding.
Causes of Gastric ulcer
- - Helicobacter pylori Infection: A bacterial infection that disrupts the stomach's protective lining, leading to ulcer formation. - Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Regular use of NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen can irritate the stomach lining, increasing ulcer risk. - Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking can erode the stomach's protective lining, making it more susceptible to ulcers. - Smoking: Smoking impairs the healing of existing ulcers and increases the risk of developing new ones. - Stress and Spicy Foods: While not direct causes, stress and spicy foods can exacerbate symptoms in individuals with existing ulcers.
Risk Factors of Gastric ulcer
- - Age: Individuals over 60 are at higher risk. - Family History: A family history of gastric ulcers can increase risk. - Use of Certain Medications: Long-term use of NSAIDs or corticosteroids. - Chronic Diseases: Conditions like cirrhosis, kidney disease, or Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Prevention of Gastric ulcer
- - Avoiding NSAIDs: Use alternative pain relievers when possible. - Moderating Alcohol Consumption: Limiting intake to reduce irritation. - Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking to promote healing and reduce risk. - Stress Management: Engaging in relaxation techniques to reduce stress levels.
Prognosis of Gastric ulcer
- With appropriate treatment, most individuals recover fully. However, if left untreated, gastric ulcers can lead to complications such as bleeding, perforation, and gastric cancer.
Complications of Gastric ulcer
- - Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Manifested by vomiting blood or passing black stools. - Perforation: A hole in the stomach or intestinal wall, leading to peritonitis. - Gastric Outlet Obstruction: Blockage preventing food from leaving the stomach.
Related Diseases of Gastric ulcer
- - Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach lining. - Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic acid reflux leading to esophageal irritation. - Gastric Cancer: A potential complication of chronic gastric ulcers.
Treatment of Gastric ulcer
- **Antibiotics**: To eradicate H. pylori infection. - **Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)**: To reduce stomach acid production. - **H2-Receptor Antagonists**: To decrease acid secretion. - **Antacids**: To neutralize existing stomach acid. - **Lifestyle Modifications**: Avoiding NSAIDs, reducing alcohol intake, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
Generics For Gastric ulcer
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Hydroxide
Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Hydroxide

Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Trisilicate
Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Trisilicate

Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Hydroxide
Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Hydroxide

Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Trisilicate
Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Trisilicate

Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Lansoprazole Kit
Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Lansoprazole Kit

Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Rabeprazole Sodium kit
Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Rabeprazole Sodium kit

Cimetidine
Cimetidine

Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate BP
Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate BP

Famotidine
Famotidine

Lansoprazole
Lansoprazole

Magaldrate + Simethicone
Magaldrate + Simethicone

Magaldrate + Simethicone Chewable
Magaldrate + Simethicone Chewable

Misoprostol
Misoprostol

Nizatidine
Nizatidine

Rabeprazole
Rabeprazole

Roxatidine
Roxatidine

Sucralfate
Sucralfate

Omeprazole + Metronidazole + Clarithromycin
Omeprazole + Metronidazole + Clarithromycin

Aluminium Hydroxide
Aluminium Hydroxide

Clarithromycin + Metronidazole + Lansoprazol
Clarithromycin + Metronidazole + Lansoprazol

Omeprazole 20mg + Sodium bicarbonate 1100mg
Omeprazole 20mg + Sodium bicarbonate 1100mg

Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Hydroxide
Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Hydroxide

Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Trisilicate
Aluminium Hydroxide + Magnesium Trisilicate

Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Hydroxide
Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Hydroxide

Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Trisilicate
Aluminium Oxide + Magnesium Trisilicate

Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Lansoprazole Kit
Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Lansoprazole Kit

Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Rabeprazole Sodium kit
Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin + Rabeprazole Sodium kit

Cimetidine
Cimetidine

Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate BP
Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate BP

Famotidine
Famotidine

Lansoprazole
Lansoprazole

Magaldrate + Simethicone
Magaldrate + Simethicone

Magaldrate + Simethicone Chewable
Magaldrate + Simethicone Chewable

Misoprostol
Misoprostol

Nizatidine
Nizatidine

Rabeprazole
Rabeprazole

Roxatidine
Roxatidine

Sucralfate
Sucralfate

Omeprazole + Metronidazole + Clarithromycin
Omeprazole + Metronidazole + Clarithromycin

Aluminium Hydroxide
Aluminium Hydroxide

Clarithromycin + Metronidazole + Lansoprazol
Clarithromycin + Metronidazole + Lansoprazol

Omeprazole 20mg + Sodium bicarbonate 1100mg
Omeprazole 20mg + Sodium bicarbonate 1100mg