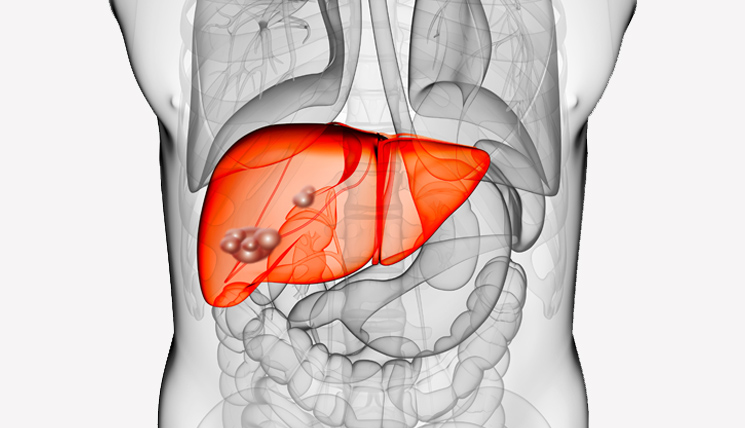
Overview Of Echinococcosis
Echinococcosis, also known as hydatid disease, is a parasitic infection caused by tapeworms of the genus *Echinococcus*. The two main types affecting humans are cystic echinococcosis (CE) and alveolar echinococcosis (AE). Humans are typically infected by ingesting *Echinococcus* eggs through contaminated food, water, or soil, or by direct contact with infected animals, particularly dogs, which are the definitive hosts of the parasite.
Symptoms of Echinococcosis
- - Abdominal Pain: Common in cases of cystic echinococcosis affecting the liver or spleen. - Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, associated with liver involvement. - Cough and Chest Pain: Respiratory symptoms if cysts affect the lungs. - Neurological Symptoms: Headaches, seizures, and other neurological symptoms when cysts affect the brain.
Causes of Echinococcosis
- -
- Ingestion of Echinococcus Eggs: Humans ingest *Echinococcus* eggs through contaminated food, water, or soil, or by handling infected animals. -
- Direct Contact with Infected Animals: Dogs and other canines are primary hosts, shedding *Echinococcus* eggs in their feces. -
- Poor Sanitation and Hygiene: Poor hygiene practices, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas, increase the risk of infection.
Risk Factors of Echinococcosis
- -
- Living in Endemic Areas: Areas where *Echinococcus* is common, especially rural regions with poor sanitation. -
- Close Contact with Dogs: Individuals who have frequent contact with dogs or work with livestock are at higher risk. -
- Occupational Exposure: Farmers, veterinarians, and abattoir workers are more likely to be exposed to *Echinococcus*. -
- Traveling to Endemic Areas: Travel to areas where the infection is prevalent increases the risk of exposure.
Prevention of Echinococcosis
- - Improved Sanitation: Ensuring access to clean water and proper waste disposal to reduce contamination. - Hygiene Practices: Regular handwashing and proper handling of animals and food. - Deworming of Dogs: Regular deworming programs for dogs in endemic areas can reduce the spread of *Echinococcus*. - Health Education: Educating at-risk populations on the risks of infection and preventive measures.
Prognosis of Echinococcosis
- - With early detection and appropriate treatment, the prognosis is generally favorable. However, untreated cases can lead to severe complications, including organ damage, infection, and even death.
Complications of Echinococcosis
- - Organ Damage: Long-term presence of cysts can impair the function of organs, particularly the liver and lungs. - Anaphylactic Shock: A severe allergic reaction caused by the rupture of cysts. - Secondary Infections: Rupture of cysts can lead to bacterial infections. - Cyst Rupture: Can spread the parasite throughout the body, leading to complications in other organs.
Related Diseases of Echinococcosis
- - Cystic Echinococcosis (Hydatidosis): A form of echinococcosis characterized by the formation of cysts in various organs. - Alveolar Echinococcosis: A more severe, often fatal form of the disease that affects the liver and can metastasize like cancer.
Treatment of Echinococcosis
- **Surgical Removal**: Surgical removal of cysts is the most common approach, particularly for cystic echinococcosis. - **Antiparasitic Drugs**: Medications such as albendazole and mebendazole help to kill the parasite, especially in cases where surgery is not possible. - **Percutaneous Techniques**: In some cases, cysts can be aspirated or treated with chemical agents under imaging guidance.
Generics For Echinococcosis
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.