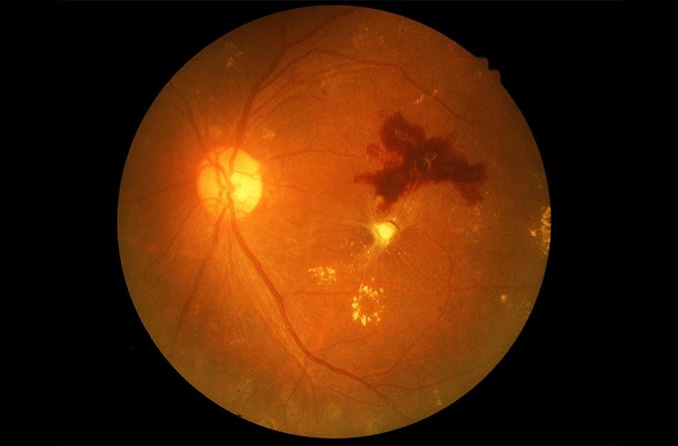
Overview Of Retinal hemorrhage
Retinal hemorrhage refers to bleeding within the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. It can occur as a result of trauma, systemic vascular disorders, or underlying health conditions. The severity of retinal hemorrhage depends on the cause and extent of the bleeding, which can lead to vision disturbances or even permanent vision loss if not properly managed.
Symptoms of Retinal hemorrhage
- - Visual Disturbances: This may include blurry vision or sudden loss of vision. - Floaters: Small, shadowy shapes that appear in the visual field, caused by blood or debris in the vitreous body. - Flashes of Light: Sudden bursts or flickers of light that may indicate retinal issues. - Pain: In some cases, retinal hemorrhage may be associated with pain, especially if due to trauma or infection.
Causes of Retinal hemorrhage
- -
- Systemic Vascular Disorders: Conditions such as hypertension and diabetes can damage retinal blood vessels, leading to bleeding within the retina. -
- Trauma: Blunt or penetrating injuries to the eye or head can result in retinal hemorrhage. -
- Blood Disorders: Disorders like anemia, clotting problems, or blood-thinning medications can increase the risk of bleeding in the retina. -
- Infections: Certain infections, particularly viral or bacterial infections, can cause inflammation and bleeding in the retina. -
- Hypoxia: Low oxygen levels in the blood can lead to changes in the retinal blood vessels, resulting in hemorrhage. -
- Retinal Vein or Artery Occlusion: Blockage of the veins or arteries in the retina can lead to increased pressure and bleeding in the retinal tissue.
Risk Factors of Retinal hemorrhage
- -
- Age: Older adults are more susceptible to age-related retinal changes and vascular conditions. -
- Chronic Health Conditions: High blood pressure, diabetes, and blood clotting disorders increase the risk of retinal hemorrhage. -
- Medications: Use of blood thinners or anticoagulants can increase the likelihood of bleeding in the retina. -
- Trauma History: Previous eye or head injuries raise the risk of retinal hemorrhage. -
- Smoking: Smoking contributes to vascular damage, increasing the risk of retinal issues, including hemorrhage.
Prevention of Retinal hemorrhage
- - Managing Chronic Health Conditions: Properly managing hypertension, diabetes, and blood clotting disorders can reduce the risk of retinal hemorrhage. - Protective Eyewear: Wearing protective glasses during activities that may pose a risk of eye injury, such as sports or construction work. - Regular Eye Exams: Routine eye examinations can help detect early signs of retinal issues and allow for timely intervention.
Prognosis of Retinal hemorrhage
- - Mild Cases: If the hemorrhage is small and caused by a treatable condition, the prognosis is usually good, with vision often returning to normal. - Severe Cases: Larger hemorrhages or those associated with conditions like retinal vein occlusion or diabetic retinopathy can lead to permanent vision loss if not managed appropriately.
Complications of Retinal hemorrhage
- - Permanent Vision Loss: In severe cases, the hemorrhage may lead to retinal scarring or retinal detachment, resulting in lasting vision problems. - Retinal Detachment: The hemorrhage can increase the risk of the retina separating from the back of the eye, a condition that requires immediate medical attention. - Macular Edema: Swelling of the macula, the central part of the retina, can occur as a result of hemorrhage and may lead to vision impairment.
Related Diseases of Retinal hemorrhage
- - Diabetic Retinopathy: A common complication of diabetes where high blood sugar damages the retinal blood vessels, potentially leading to hemorrhage. - Hypertensive Retinopathy: Retinal changes caused by high blood pressure, which can lead to bleeding in the retina. - Retinal Vein Occlusion: A blockage in the retinal vein that can cause retinal hemorrhage and other complications. - Retinal Artery Occlusion: A blockage in the retinal artery that can cause ischemia and bleeding in the retina.
Treatment of Retinal hemorrhage
- **Treating the Underlying Cause**: If the hemorrhage is due to conditions like hypertension or diabetes, controlling these conditions is crucial. - **Laser Therapy**: In some cases, laser treatment can be used to seal leaking blood vessels and prevent further bleeding. - **Vitrectomy**: A surgical procedure to remove the vitreous gel if hemorrhage is severe or persists. - **Medications**: Corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed if inflammation is involved.
Generics For Retinal hemorrhage
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Adrenochrome Monosemicarbazone
Adrenochrome Monosemicarbazone

Adrenochrome Monosemicarbazone
Adrenochrome Monosemicarbazone