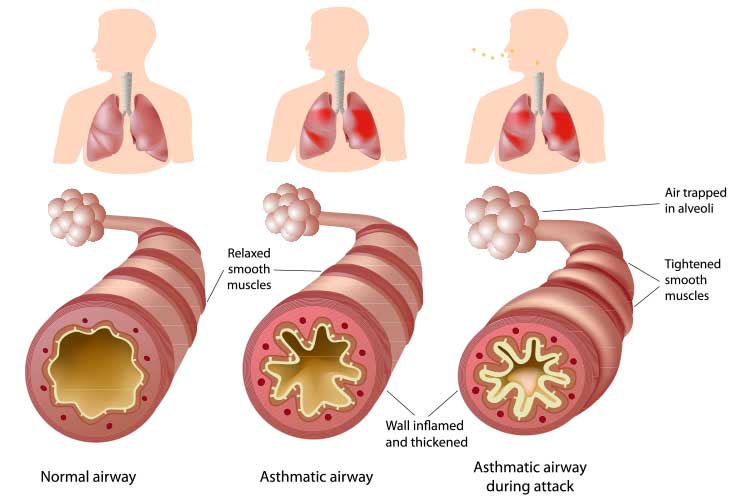
Overview Of Acute asthma
Acute asthma refers to a sudden worsening or flare-up of asthma symptoms due to increased airway inflammation and constriction. It can lead to difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and increased respiratory rate. If not treated promptly, acute asthma attacks can be life-threatening. The condition requires immediate medical attention to manage symptoms and prevent further complications.
Symptoms of Acute asthma
- - Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, often triggered by physical activity or at night, is a hallmark symptom of an acute asthma attack. - Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound when exhaling due to constricted airways. - Coughing: A persistent cough, particularly at night or in the early morning, is common during an acute asthma attack. - Chest Tightness: A sensation of pressure or tightness in the chest is often experienced during an asthma exacerbation. - Rapid Breathing: Increased respiratory rate in an attempt to compensate for airway obstruction. - Difficulty Speaking: In severe cases, patients may find it hard to speak in full sentences due to breathlessness.
Causes of Acute asthma
- -
- Allergens: Exposure to common allergens such as pollen, dust mites, mold, or pet dander can trigger acute asthma symptoms. -
- Respiratory Infections: Viral or bacterial infections, especially respiratory infections like the flu or cold, can worsen asthma symptoms. -
- Air Pollution: Exposure to pollutants such as smoke, chemical fumes, or strong odors can exacerbate asthma attacks. -
- Physical Activity: Intense physical exercise, particularly in cold or dry air, can trigger acute asthma symptoms in some individuals. -
- Weather Conditions: Sudden changes in temperature, high humidity, or cold air can lead to an asthma exacerbation. -
- Medications: Certain drugs, like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can worsen asthma symptoms in some people.
Risk Factors of Acute asthma
- -
- Uncontrolled Asthma: Poor management of asthma with inadequate medication or failure to avoid triggers increases the risk of acute attacks. -
- Exposure to Triggers: Regular contact with asthma triggers, such as allergens, pollutants, or respiratory infections, raises the likelihood of exacerbations. -
- Respiratory Infections: Individuals with asthma who have recently had respiratory illnesses are at higher risk for acute asthma attacks. -
- Allergic Conditions: Those with other allergic conditions, like allergic rhinitis or eczema, may experience more frequent and severe asthma attacks. -
- Environmental Factors: Living in areas with high levels of air pollution or allergens can increase the risk of asthma flare-ups.
Prevention of Acute asthma
- - Adherence to Medication: Taking prescribed asthma medications consistently, including inhaled corticosteroids and bronchodilators, is key to preventing acute attacks. - Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding asthma triggers such as allergens, air pollution, and respiratory infections can help reduce the frequency of attacks. - Regular Monitoring: Monitoring lung function with a peak flow meter helps identify early signs of worsening asthma and prompt intervention. - Vaccinations: Keeping up-to-date with flu and pneumonia vaccinations can help prevent respiratory infections that may trigger asthma exacerbations. - Education: Learning to recognize early symptoms of an asthma attack allows for prompt use of rescue inhalers and other treatments to manage the condition.
Prognosis of Acute asthma
- - With prompt treatment, most individuals recover fully from an acute asthma attack. However, untreated or severe attacks can lead to complications, including respiratory failure, and may be life-threatening. Chronic asthma exacerbations can lead to a progressive decline in lung function if not properly managed.
Complications of Acute asthma
- - Respiratory Failure: In severe asthma attacks, the airways may become so constricted that the lungs are unable to provide adequate oxygen, leading to respiratory failure. - Pneumothorax: In extreme cases, the intense pressure on the lungs can cause a collapsed lung (pneumothorax). - Cardiac Arrest: Severe and prolonged asthma attacks can lead to complications like cardiac arrest, though this is rare.
Related Diseases of Acute asthma
- - Allergic Rhinitis: A condition in which the nasal passages become inflamed due to allergies, often co-occurring with asthma. - Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Acid reflux can trigger asthma symptoms or exacerbate existing asthma. - Sinusitis: Chronic sinus inflammation can increase the frequency of asthma attacks. - Obesity: Excess weight can make asthma symptoms worse and increase the severity of asthma attacks. - Sleep Apnea: Obstructive sleep apnea may worsen asthma symptoms and affect overall asthma control.
Treatment of Acute asthma
- **Short-Acting Beta-Agonists (SABAs)**: Inhalers such as albuterol provide immediate relief by relaxing the muscles around the airways, improving airflow. - **Corticosteroids**: Oral or intravenous corticosteroids, like prednisone, are used to reduce inflammation in the airways. - **Oxygen Therapy**: Oxygen may be administered if blood oxygen levels drop below normal. - **Anticholinergics**: Medications like ipratropium can help open the airways by blocking acetylcholine, which causes constriction. - **Magnesium Sulfate**: In severe cases, intravenous magnesium can help relax the muscles of the airways and improve airflow.
Generics For Acute asthma
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Aminophylline
Aminophylline

Bambuterol Hydrochloride
Bambuterol Hydrochloride

Beclomethasone Dipropionate
Beclomethasone Dipropionate

Budesonide
Budesonide

Budesonide + Formoterol Fumarate
Budesonide + Formoterol Fumarate

Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate
Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate

Ephedrine Hydrochloride
Ephedrine Hydrochloride

Formoterol Fumarate
Formoterol Fumarate

Hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone

Ipratropium Bromide + Salbutamol
Ipratropium Bromide + Salbutamol

Levosalbutamol
Levosalbutamol

Prednisolone
Prednisolone

Terbutaline Sulphate
Terbutaline Sulphate

Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone

Salbutamol
Salbutamol

Doxofylline
Doxofylline

Aminophylline
Aminophylline

Bambuterol Hydrochloride
Bambuterol Hydrochloride

Beclomethasone Dipropionate
Beclomethasone Dipropionate

Budesonide
Budesonide

Budesonide + Formoterol Fumarate
Budesonide + Formoterol Fumarate

Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate
Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate

Ephedrine Hydrochloride
Ephedrine Hydrochloride

Formoterol Fumarate
Formoterol Fumarate

Hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone

Ipratropium Bromide + Salbutamol
Ipratropium Bromide + Salbutamol

Levosalbutamol
Levosalbutamol

Prednisolone
Prednisolone

Terbutaline Sulphate
Terbutaline Sulphate

Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone

Salbutamol
Salbutamol

Doxofylline
Doxofylline