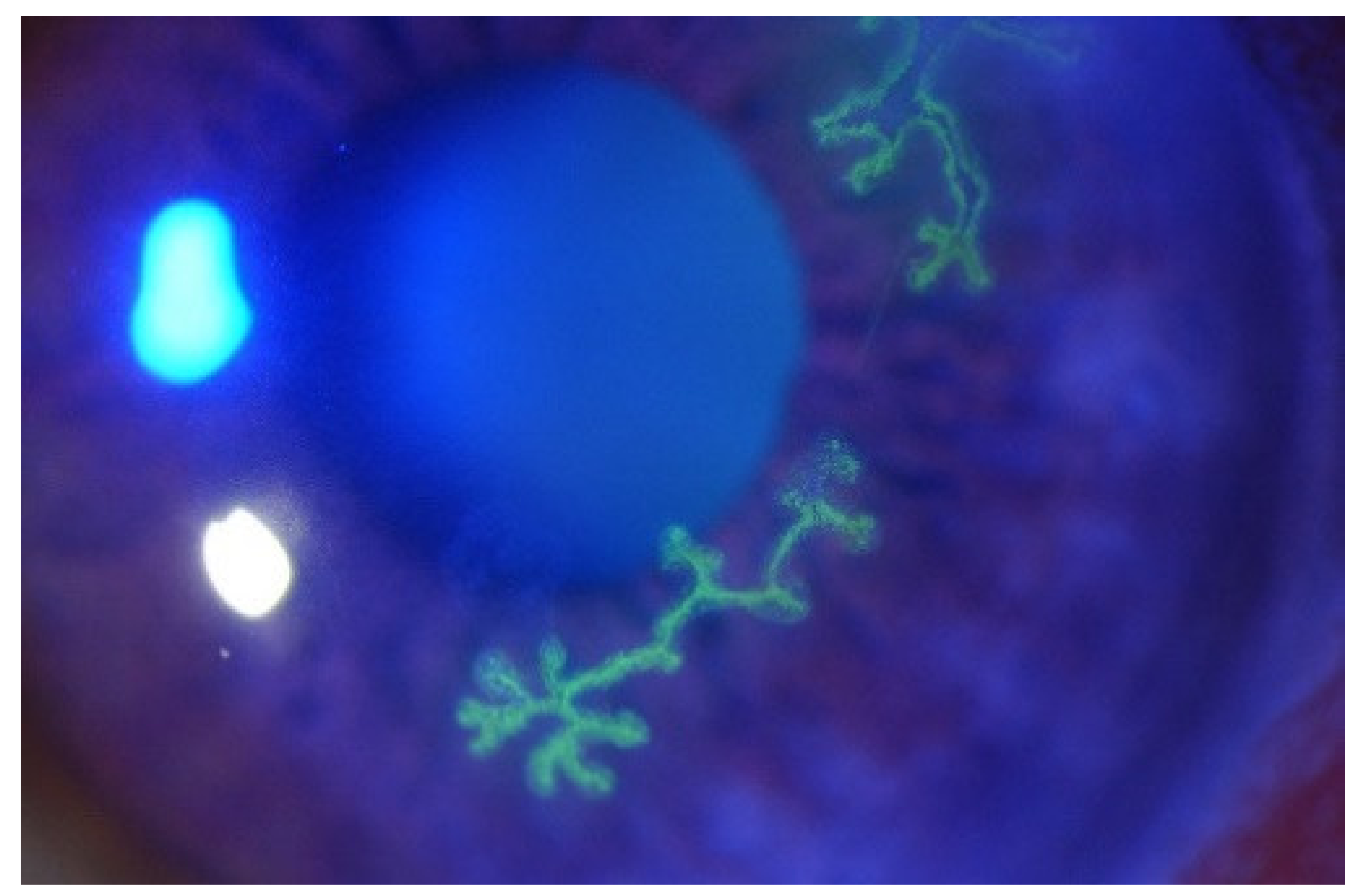
Overview Of Herpes simplex keratitis
Herpes simplex keratitis is an eye infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), most commonly HSV-1. It affects the cornea, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential vision loss if untreated. The infection can recur as the virus remains dormant in nerve cells and may reactivate, especially under conditions such as stress or weakened immunity.
Symptoms of Herpes simplex keratitis
- - Eye pain, irritation, or discomfort. - Redness of the eye and surrounding areas. - Blurred vision or decreased visual acuity. - Sensitivity to light (photophobia). - Watery or discharge from the eye. - Recurrent episodes of eye infection.
Causes of Herpes simplex keratitis
- - Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): - HSV-1: Primary cause of herpes simplex keratitis, typically spread through direct contact with infected secretions or eye fluids. - HSV-2: Less commonly causes ocular infections, but can affect the eye through genital contact.
Risk Factors of Herpes simplex keratitis
- - Previous HSV Infection: Individuals with a history of cold sores or genital herpes are at higher risk. - Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV or immunosuppressive treatments can increase susceptibility to reactivation. - Contact Lens Use: Increases risk of corneal infection. - Eye Trauma or Surgery: Can trigger reactivation of dormant HSV.
Prevention of Herpes simplex keratitis
- - Avoid Direct Eye Contact: Do not touch the eye with unwashed hands, and avoid sharing towels or makeup. - Manage Cold Sores: Effective treatment of oral herpes can reduce the risk of ocular involvement. - Contact Lens Hygiene: Regular cleaning and proper use of contact lenses reduce the risk of infection. - Antiviral Suppression: Long-term antiviral treatment may be recommended for individuals with frequent recurrences.
Prognosis of Herpes simplex keratitis
- With prompt antiviral treatment, herpes simplex keratitis can often be controlled. However, recurrent infections may lead to scarring of the cornea, which can cause permanent vision problems or blindness if not treated effectively.
Complications of Herpes simplex keratitis
- - Corneal Scarring: Damage to the cornea can lead to vision impairment or blindness. - Glaucoma: Inflammation caused by the infection may increase intraocular pressure. - Chronic Recurrent Infection: HSV may reactivate and cause repeated episodes. - Secondary Bacterial Infection: Complications from the use of topical treatments or associated corneal damage.
Related Diseases of Herpes simplex keratitis
- - Herpes Simplex Virus (Cold Sores): Oral infection caused by HSV-1, which can spread to the eyes. - Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus: Reactivation of varicella zoster virus affecting the eye. - Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): Can be caused by HSV, presenting as eye redness and discharge.
Treatment of Herpes simplex keratitis
- **Antiviral Medications**: - Oral antivirals (e.g., acyclovir, valacyclovir) for severe cases. - Topical antivirals (e.g., trifluridine, ganciclovir) for direct application to the eye. - **Corticosteroids**: Used cautiously to reduce inflammation but only under close medical supervision, as they can worsen the infection. - **Lubricating Eye Drops**: Help alleviate dryness and discomfort.
Generics For Herpes simplex keratitis
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Acyclovir 3% Eye prep
Acyclovir 3% Eye prep

Idoxuridine 0.1% Eye prep
Idoxuridine 0.1% Eye prep

Trifluridine 1% Eye prep
Trifluridine 1% Eye prep

Valacyclovir
Valacyclovir

Famciclovir INN
Famciclovir INN

Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye prep
Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye prep

Acyclovir 3% Eye prep
Acyclovir 3% Eye prep

Idoxuridine 0.1% Eye prep
Idoxuridine 0.1% Eye prep

Trifluridine 1% Eye prep
Trifluridine 1% Eye prep

Valacyclovir
Valacyclovir

Famciclovir INN
Famciclovir INN

Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye prep
Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye prep