Overview Of Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
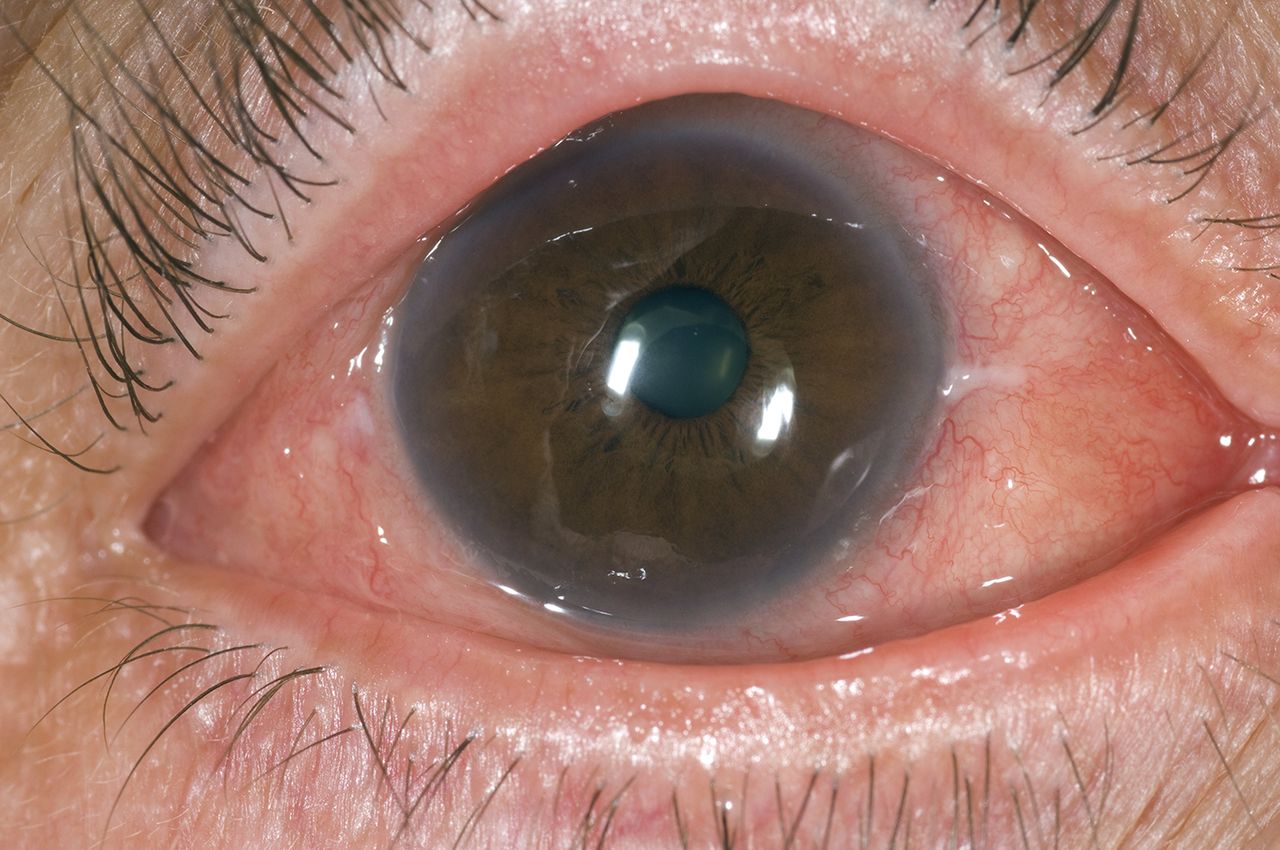
Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye refer to a range of disorders where the eye becomes inflamed due to an allergic reaction or other inflammatory processes. These conditions are common and can cause symptoms such as redness, itching, swelling, pain, and visual disturbances. The most prevalent allergic condition affecting the eyes is allergic conjunctivitis, which occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens like pollen, dust, or pet dander. Inflammatory conditions can be caused by autoimmune diseases, infections, or other factors that lead to inflammation in different parts of the eye, including the cornea, conjunctiva, iris, or optic nerve. These conditions can be acute or chronic, and while some resolve with minimal treatment, others may require long-term management to prevent complications like vision loss or scarring.
Symptoms of Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
- The symptoms of allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye can vary based on the underlying cause but often include:
- Redness: Both allergic and inflammatory eye conditions typically result in noticeable redness, as the blood vessels in the eye become dilated.
- Itching: Itching is a hallmark symptom of allergic reactions affecting the eye, particularly in allergic conjunctivitis.
- Swelling: Swelling of the eyelids, conjunctiva, or surrounding tissues may occur, often making the eyes appear puffy.
- Tearing: Excessive tearing or watery eyes is a common symptom, especially in allergic conjunctivitis.
- Discharge: A clear, watery discharge is typical in allergic conditions, while a yellow or greenish discharge may indicate bacterial infection.
- Pain or Sensitivity: Inflammatory eye conditions such as uveitis or scleritis can cause pain, sensitivity to light (photophobia), and a feeling of pressure in the eye.
- Blurred Vision: Inflammation affecting the cornea, iris, or retina can result in blurred vision or a decrease in visual acuity.
- Foreign Body Sensation: Inflammation or dryness can cause a feeling that something is in the eye, even if there is no actual foreign body present.
- Burning Sensation: Allergic reactions can lead to a burning sensation in the eyes, especially when exposed to allergens or irritants.
Causes of Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
- The causes of allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye can be categorized into two main groups:
- Allergic Reactions: - Pollen: Seasonal allergies caused by pollen from trees, grasses, or weeds are common triggers for allergic conjunctivitis. - Dust and Mold: Dust mites, mold spores, and pet dander can also trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. - Animal Allergens: Proteins found in pet saliva, dander, or urine can cause allergic eye inflammation in individuals with sensitivities to animals. - Cosmetic Products: Some eye makeup or facial products may contain chemicals that trigger allergic reactions. - Contact Lenses: The use of contact lenses, particularly if worn for long periods or not cleaned properly, can lead to allergic reactions in the eyes.
- Inflammatory Conditions: - Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Sjögren’s syndrome can cause chronic inflammation in the eye, leading to conditions like uveitis or keratoconjunctivitis. - Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause eye inflammation. For example, viral conjunctivitis, caused by adenoviruses, or bacterial infections from organisms like Streptococcus or Staphylococcus. - Trauma or Injury: Physical injuries to the eye, such as scratches or foreign body penetration, can trigger inflammation in response to the injury. - Drug Reactions: Certain medications can cause allergic reactions that lead to eye inflammation, including topical eye drops or systemic medications.
Risk Factors of Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
- Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye:
- Allergy History: Individuals with a history of seasonal or environmental allergies are more likely to experience allergic eye conditions.
- Contact Lens Use: Wearing contact lenses increases the risk of eye infections and allergic reactions, especially if the lenses are not properly cared for.
- Immune System Disorders: People with autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus are at higher risk for developing inflammatory eye conditions like uveitis or scleritis.
- Infections: Previous or recurrent eye infections can increase susceptibility to other inflammatory eye conditions.
- Exposure to Allergens: Living in environments with high pollen counts, dust, or pet dander, or working in conditions where irritants are present, increases the risk of developing allergic conjunctivitis.
- Age and Gender: Certain inflammatory eye conditions, like dry eye syndrome, are more common in older adults and women.
- Medications: Long-term use of certain medications, such as those for glaucoma, can increase the risk of inflammation in the eye.
Prevention of Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
- Preventing allergic and inflammatory eye conditions involves managing underlying risk factors and reducing exposure to triggers:
- Allergen Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding known allergens, such as pollen, dust, or pet dander, can help reduce the frequency and severity of allergic reactions.
- Proper Hygiene: Regular hand washing and avoiding touching the eyes with unclean hands can help prevent infections.
- Lubrication: Using lubricating eye drops or artificial tears can help maintain eye moisture and reduce irritation, especially in dry environments.
- Protective Eyewear: Wearing sunglasses or protective goggles can help shield the eyes from environmental irritants, UV rays, or foreign bodies.
- Regular Eye Exams: Regular eye check-ups can help detect early signs of inflammation or infection, leading to prompt treatment and reducing the risk of complications.
Prognosis of Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
- The prognosis for allergic and inflammatory eye conditions largely depends on the cause and severity of the condition.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: This condition is usually self-limited and resolves with appropriate treatment, such as antihistamines or corticosteroid drops. Long-term management involves avoiding allergens.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Conditions like uveitis or scleritis can be more serious and may require ongoing treatment. With early diagnosis and treatment, most people with inflammatory eye conditions can achieve good outcomes and avoid complications like vision loss. However, chronic or untreated inflammation may lead to complications, including cataracts, glaucoma, or retinal damage.
- Infectious Conditions: The prognosis for bacterial, viral, or fungal infections affecting the eye is generally good with timely treatment. However, untreated infections can lead to serious complications, including permanent vision loss.
Complications of Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
- Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye can lead to various complications if left untreated:
- Vision Loss: Severe inflammation can damage the cornea, retina, or optic nerve, leading to permanent vision impairment or blindness.
- Chronic Dry Eye: Chronic inflammation can lead to reduced tear production, resulting in persistent dryness and irritation.
- Cataracts: Prolonged corticosteroid use for inflammatory conditions can increase the risk of cataract formation.
- Glaucoma: Untreated inflammation can raise intraocular pressure, leading to glaucoma, a condition that can cause optic nerve damage and vision loss.
- Corneal Scarring: Inflammatory conditions affecting the cornea, such as keratitis, can result in scarring, leading to blurred vision or permanent visual impairment.
Related Diseases of Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
- Dry Eye Syndrome: A common condition where the eyes do not produce enough tears, leading to irritation and inflammation.
- Conjunctivitis: Often referred to as "pink eye," this is an inflammation of the conjunctiva that can be caused by allergies, infections, or irritants.
- Keratitis: Inflammation of the cornea, often due to infections, autoimmune conditions, or trauma.
- Uveitis: An inflammation of the uveal tract of the eye, which includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid.
- Scleritis: Inflammation of the sclera, the white outer layer of the eye, often related to autoimmune diseases.
- Blepharitis: Inflammation of the eyelid margins, often associated with bacterial infections or skin conditions like rosacea.
Treatment of Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
Treatment for allergic and inflammatory eye conditions depends on the underlying cause and may include: 1. **Allergic Conditions**: - **Antihistamines**: Oral antihistamines or antihistamine eye drops can help alleviate itching and redness associated with allergic conjunctivitis. - **Mast Cell Stabilizers**: These medications help prevent the release of histamine and other chemicals involved in allergic reactions. - **Decongestant Eye Drops**: These help reduce redness by constricting blood vessels in the conjunctiva. - **Corticosteroids**: In severe allergic reactions, corticosteroid eye drops may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage. - **Avoiding Allergens**: Managing exposure to known allergens (such as pollen or pet dander) is key to reducing symptoms. 2. **Inflammatory Conditions**: - **Corticosteroids**: Inflammatory conditions like uveitis, scleritis, or keratitis are often treated with corticosteroid eye drops or oral steroids to reduce inflammation. - **Immunosuppressive Therapy**: For autoimmune-related inflammation, immunosuppressive drugs such as methotrexate or biologic therapies may be used to modulate the immune system. - **Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)**: These can be used to reduce pain and swelling in conditions like scleritis or episcleritis. - **Antibiotics or Antivirals**: In cases of infectious conjunctivitis or other eye infections, topical or oral antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals may be necessary. - **Lubricating Eye Drops**: These are often used to manage dry eyes or irritation caused by inflammatory conditions. 3. **Surgical Interventions**: In rare cases, surgical intervention may be required to treat complications arising from severe inflammation, such as corneal scarring or glaucoma.
Generics For Allergic and inflammatory conditions of the eye
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Betamethasone 0.1% E E & Nasal prep
Betamethasone 0.1% E E & Nasal prep

Betamethasone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% E E prep
Betamethasone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% E E prep

Cyclosporine 0.05% Eye prep
Cyclosporine 0.05% Eye prep

Fluormetholone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% Eye prep
Fluormetholone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% Eye prep

Fluorometholone 0.1 % Eye prep
Fluorometholone 0.1 % Eye prep

Fluorometholone 0.1% + Gentamicin 0.3% Eye prep
Fluorometholone 0.1% + Gentamicin 0.3% Eye prep

Fluorometholone 0.1% + Tetrahydrozoline Hydrochloride 0.025% Eye prep
Fluorometholone 0.1% + Tetrahydrozoline Hydrochloride 0.025% Eye prep

Gentamicin 0.3% + Hydrocortisone Acetate 1% Eye prep
Gentamicin 0.3% + Hydrocortisone Acetate 1% Eye prep

Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% Eye prep
Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% Eye prep

Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3% Eye prep
Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3% Eye prep

Olopatadine 0.1% Eye prep
Olopatadine 0.1% Eye prep

Olopatadine 0.2% Eye prep
Olopatadine 0.2% Eye prep

Alcaftadine
Alcaftadine

Betamethasone 0.1% E E & Nasal prep
Betamethasone 0.1% E E & Nasal prep

Betamethasone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% E E prep
Betamethasone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% E E prep

Cyclosporine 0.05% Eye prep
Cyclosporine 0.05% Eye prep

Fluormetholone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% Eye prep
Fluormetholone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% Eye prep

Fluorometholone 0.1 % Eye prep
Fluorometholone 0.1 % Eye prep

Fluorometholone 0.1% + Gentamicin 0.3% Eye prep
Fluorometholone 0.1% + Gentamicin 0.3% Eye prep

Fluorometholone 0.1% + Tetrahydrozoline Hydrochloride 0.025% Eye prep
Fluorometholone 0.1% + Tetrahydrozoline Hydrochloride 0.025% Eye prep

Gentamicin 0.3% + Hydrocortisone Acetate 1% Eye prep
Gentamicin 0.3% + Hydrocortisone Acetate 1% Eye prep

Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% Eye prep
Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% Eye prep

Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3% Eye prep
Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3% Eye prep

Olopatadine 0.1% Eye prep
Olopatadine 0.1% Eye prep

Olopatadine 0.2% Eye prep
Olopatadine 0.2% Eye prep

Alcaftadine
Alcaftadine