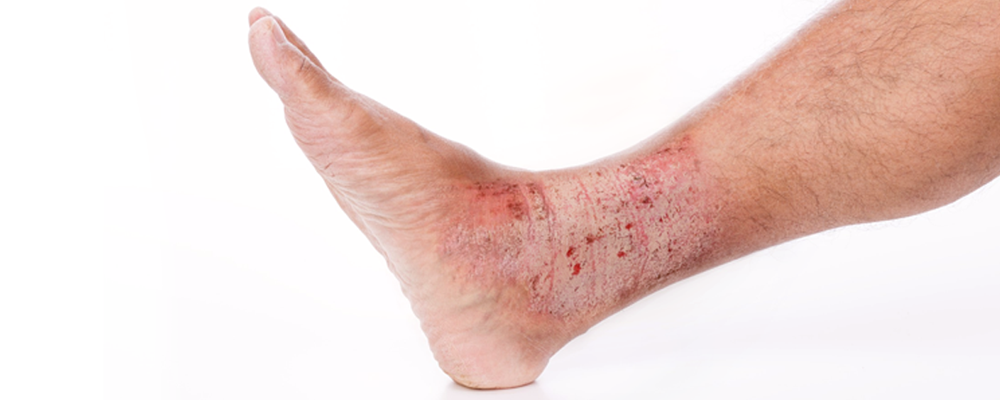
Overview Of Lichen simplex
Lichen simplex, also known as lichen simplex chronicus (LSC), is a chronic skin condition characterized by localized areas of thickened, leathery skin caused by repeated scratching or rubbing. It is a type of neurodermatitis, where the itch-scratch cycle perpetuates the condition. The affected skin often appears hyperpigmented, lichenified (thickened), and may have exaggerated skin markings. Common sites include the neck, wrists, ankles, and genital areas. Lichen simplex is not contagious but can cause significant discomfort and psychological distress due to persistent itching and the visible nature of the lesions. The condition is often associated with underlying skin disorders, such as eczema or psoriasis, or psychological factors like stress and anxiety.
Symptoms of Lichen simplex
- The hallmark symptom of lichen simplex is intense itching, which leads to scratching and the development of thickened, leathery skin patches. These patches are often:
- Hyperpigmented: Darker than the surrounding skin due to chronic inflammation.
- Lichenified: Thickened with exaggerated skin markings.
- Scaly or Rough: The surface may be dry and flaky.
- Localized: Commonly affects the neck, wrists, ankles, scalp, and genital areas.
- Pruritic: Itching is often worse at night or during periods of stress. The persistent itching and scratching can lead to secondary infections or scarring.
Causes of Lichen simplex
- The primary cause of lichen simplex is repeated scratching or rubbing of the skin, which leads to thickening and further itching, creating a vicious cycle. Underlying factors that contribute to the development of lichen simplex include:
- Skin Conditions: Pre-existing conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or contact dermatitis can predispose individuals to lichen simplex.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive behaviors can exacerbate scratching.
- Environmental Irritants: Exposure to allergens, harsh soaps, or tight clothing can trigger itching.
- Dry Skin: Lack of moisture in the skin can increase susceptibility to itching and scratching.
- Nerve Dysfunction: Abnormal nerve signaling in the skin may contribute to chronic itching.
Risk Factors of Lichen simplex
- Several factors increase the risk of developing lichen simplex:
- Pre-existing Skin Conditions: Eczema, psoriasis, or contact dermatitis.
- Psychological Stress: Anxiety, depression, or obsessive-compulsive tendencies.
- Dry Skin: Lack of proper skin hydration.
- Environmental Irritants: Exposure to allergens or harsh chemicals.
- Age and Gender: More common in adults, particularly women.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of atopic dermatitis or other skin disorders.
Prevention of Lichen simplex
- Preventing lichen simplex involves managing triggers and maintaining skin health:
- Avoid Scratching: Breaking the itch-scratch cycle is crucial.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated reduces itching.
- Manage Stress: Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or therapy can help.
- Identify Triggers: Avoiding allergens or irritants that exacerbate itching.
- Wear Soft Clothing: Loose, breathable fabrics reduce friction and irritation.
- Seek Early Treatment: Addressing underlying skin conditions promptly can prevent lichen simplex.
Prognosis of Lichen simplex
- The prognosis of lichen simplex depends on the ability to break the itch-scratch cycle and manage underlying triggers. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, most patients experience significant improvement. However, recurrence is common, particularly if stress or environmental irritants are not adequately addressed. Chronic cases may lead to permanent skin changes, such as hyperpigmentation or scarring. Regular follow-up with a dermatologist and adherence to treatment are essential for maintaining control of the condition.
Complications of Lichen simplex
- Lichen simplex can lead to several complications, including:
- Secondary Infections: Scratching can introduce bacteria, leading to infections like cellulitis.
- Scarring: Chronic scratching can cause permanent skin damage.
- Sleep Disturbances: Nighttime itching can disrupt sleep and affect quality of life.
- Psychological Impact: The visible nature of the lesions and persistent itching can lead to anxiety or depression.
- Chronic Skin Changes: Thickened, hyperpigmented skin may become permanent if untreated.
Related Diseases of Lichen simplex
- Lichen simplex is related to several other skin conditions, including:
- Atopic Dermatitis: A chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by itching and eczema.
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune condition causing scaly, inflamed skin patches.
- Prurigo Nodularis: A condition characterized by intensely itchy nodules.
- Contact Dermatitis: Skin inflammation caused by exposure to irritants or allergens.
- Nummular Eczema: Coin-shaped eczema patches that can resemble lichen simplex. Understanding these related diseases aids in differential diagnosis and comprehensive management.
Treatment of Lichen simplex
The treatment of lichen simplex focuses on breaking the itch-scratch cycle and addressing underlying causes. Key approaches include: 1. **Topical Corticosteroids**: To reduce inflammation and itching. 2. **Moisturizers**: To hydrate the skin and reduce dryness. 3. **Antihistamines**: To relieve itching, particularly at night. 4. **Behavioral Therapy**: To address stress, anxiety, or compulsive scratching. 5. **Barrier Creams**: To protect the skin from irritants. 6. **Phototherapy**: In refractory cases, UV light therapy may be beneficial. 7. **Systemic Medications**: For severe cases, oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be considered. Patient education on avoiding scratching and managing triggers is crucial for long-term control.
Generics For Lichen simplex
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Betamethasone valerate 0.01% Topical
Betamethasone valerate 0.01% Topical

Betamethasone 0.1% + Fusidic Acid 2% Topical
Betamethasone 0.1% + Fusidic Acid 2% Topical

Betamethasone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% Topical
Betamethasone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% Topical

Doxepin 5% Topical
Doxepin 5% Topical

Salicylic Acid 6% & 12% Topical
Salicylic Acid 6% & 12% Topical

Betamethasone valerate 0.05% Topical
Betamethasone valerate 0.05% Topical

Betamethasone valerate 0.01% Topical
Betamethasone valerate 0.01% Topical

Betamethasone 0.1% + Fusidic Acid 2% Topical
Betamethasone 0.1% + Fusidic Acid 2% Topical

Betamethasone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% Topical
Betamethasone 0.1% + Neomycin Sulphate 0.5% Topical

Doxepin 5% Topical
Doxepin 5% Topical

Salicylic Acid 6% & 12% Topical
Salicylic Acid 6% & 12% Topical

Betamethasone valerate 0.05% Topical
Betamethasone valerate 0.05% Topical