Overview Of Skin irritations
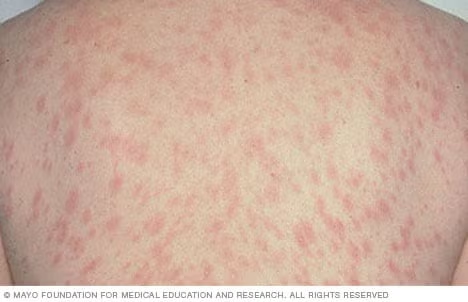
Skin irritations refer to a broad range of conditions that cause discomfort, redness, itching, or inflammation of the skin. These irritations can result from various causes, including allergic reactions, infections, environmental factors, or underlying medical conditions. Common examples include contact dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, insect bites, and sunburn. Skin irritations can affect any part of the body and range from mild to severe. While many skin irritations are temporary and resolve with proper care, some may indicate chronic conditions requiring long-term management. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. ---
Symptoms of Skin irritations
- The symptoms of skin irritations vary depending on the cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include redness, itching, swelling, and pain or tenderness in the affected area. Rashes, blisters, dryness, or flaking may also occur. In some cases, skin irritations can lead to oozing, crusting, or scarring. Systemic symptoms, such as fever or fatigue, may accompany irritations caused by infections or allergic reactions. The location and pattern of the irritation (e.g., localized or widespread) provide clues to the underlying cause. Early recognition of symptoms helps in prompt diagnosis and treatment. ---
Causes of Skin irritations
- Skin irritations can be caused by a wide range of factors. Allergic reactions, such as contact dermatitis from exposure to irritants like poison ivy, cosmetics, or detergents, are common causes. Infections, including bacterial (e.g., cellulitis), fungal (e.g., athlete’s foot), or viral (e.g., herpes), can also lead to skin irritation. Environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, or UV radiation, contribute to conditions like sunburn or dry skin. Chronic skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea, cause recurring irritations. Systemic diseases, such as liver or kidney disorders, may also manifest as skin irritations. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment. ---
Risk Factors of Skin irritations
- Several factors increase the risk of developing skin irritations. A history of allergies or sensitive skin predisposes individuals to allergic reactions or contact dermatitis. Occupational exposure to irritants, such as chemicals or detergents, elevates the risk in certain professions. Environmental factors, such as dry or cold weather, can exacerbate skin dryness or irritation. Chronic skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, increase susceptibility to recurring irritations. Poor hygiene, compromised immunity, or underlying systemic diseases also contribute to the risk. Preventive measures, such as avoiding known irritants and maintaining skin hydration, reduce the likelihood of skin irritations. ---
Prevention of Skin irritations
- Preventing skin irritations involves identifying and avoiding triggers, maintaining skin health, and adopting protective measures. For allergic reactions, avoiding known irritants, such as certain cosmetics or plants, is key. Using gentle skincare products and moisturizers helps maintain the skin barrier. Wearing protective clothing, such as gloves or long sleeves, reduces exposure to environmental irritants or UV radiation. Practicing good hygiene and promptly treating minor skin issues prevent infections. Educating individuals about skin health and preventive measures reduces the incidence of skin irritations. ---
Prognosis of Skin irritations
- The prognosis for skin irritations varies depending on the cause and severity of the condition. Most irritations, such as mild allergic reactions or sunburn, resolve within a few days to weeks with proper care. Chronic conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, require long-term management but can be controlled with appropriate treatment. Infections, if treated promptly, typically resolve without complications. Early diagnosis and adherence to treatment plans improve outcomes and prevent recurrence. Public health initiatives promoting skin health and education about preventive measures further enhance prognosis. ---
Complications of Skin irritations
- Untreated or poorly managed skin irritations can lead to several complications. Excessive scratching can cause skin damage, infections, or scarring. Chronic irritations, such as eczema, may lead to lichenification (thickening of the skin) or psychological distress. Systemic infections or allergic reactions can cause widespread symptoms, such as fever or organ involvement. In severe cases, skin irritations may indicate underlying systemic diseases requiring further evaluation. Early intervention and proper wound care are essential to prevent complications and ensure a full recovery. ---
Related Diseases of Skin irritations
- Skin irritations are closely related to various dermatological and systemic conditions. Allergic contact dermatitis shares similarities with other allergic reactions, such as hives or atopic dermatitis. Infections, such as cellulitis or fungal infections, can cause similar symptoms. Chronic skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea, are associated with recurring irritations. Systemic diseases, such as liver or kidney disorders, may manifest as skin irritations. Understanding these related diseases is important for comprehensive diagnosis and management. Preventive measures for skin irritations also reduce the risk of other skin conditions. ---
Treatment of Skin irritations
The treatment of skin irritations depends on the underlying cause. For allergic reactions, avoiding the irritant and using topical corticosteroids or antihistamines can alleviate symptoms. Infections may require antibiotics, antifungals, or antivirals. Moisturizers and emollients are essential for managing dry skin or eczema. Inflammatory conditions, such as psoriasis, may be treated with topical or systemic medications, including biologics. Cool compresses, oatmeal baths, or over-the-counter pain relievers can provide symptomatic relief. Proper wound care and hygiene prevent secondary infections. Early and targeted treatment improves outcomes and prevents complications. ---
Generics For Skin irritations
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Calamine 15% + Zinc Oxide 5%
Calamine 15% + Zinc Oxide 5%

Cetrimide 0.5% + Chlorhexidine Hydrochloride 0.1%
Cetrimide 0.5% + Chlorhexidine Hydrochloride 0.1%

Hydrocortisone 1% Topical
Hydrocortisone 1% Topical

Hydrocortisone Acetate 2.5% + Pramoxine 1% Topical
Hydrocortisone Acetate 2.5% + Pramoxine 1% Topical

Menthol 1% + Pramoxine Hydrochloride 1% Topical
Menthol 1% + Pramoxine Hydrochloride 1% Topical

Calamine 15% + Zinc Oxide 5%
Calamine 15% + Zinc Oxide 5%

Cetrimide 0.5% + Chlorhexidine Hydrochloride 0.1%
Cetrimide 0.5% + Chlorhexidine Hydrochloride 0.1%

Hydrocortisone 1% Topical
Hydrocortisone 1% Topical

Hydrocortisone Acetate 2.5% + Pramoxine 1% Topical
Hydrocortisone Acetate 2.5% + Pramoxine 1% Topical

Menthol 1% + Pramoxine Hydrochloride 1% Topical
Menthol 1% + Pramoxine Hydrochloride 1% Topical