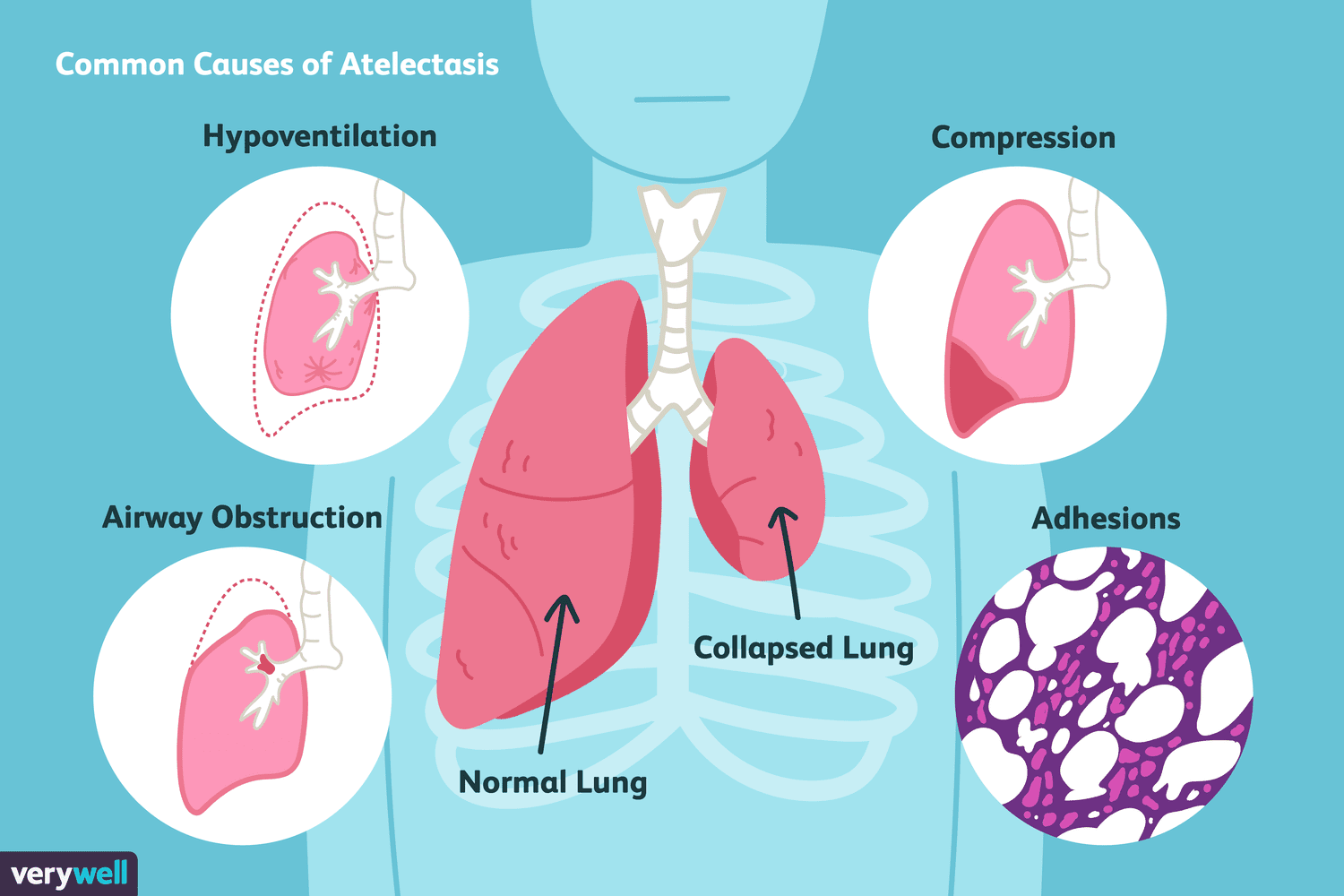
Overview Of Atelectasis
Atelectasis is a condition characterized by the partial or complete collapse of a lung or a section of a lung. This occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung deflate, preventing normal oxygen exchange. Atelectasis can affect one or both lungs and can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of lung collapse and the underlying cause. Atelectasis is not a disease itself but rather a complication of other conditions or medical procedures. It is commonly seen after surgery, particularly chest or abdominal surgery, due to restricted breathing or the effects of anesthesia. Other causes include blockages in the airways, lung infections, or pressure on the lung from outside sources, such as tumors or fluid buildup. Symptoms of atelectasis may include shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and a persistent cough. In mild cases, atelectasis may resolve on its own, but severe cases require medical intervention to prevent complications such as pneumonia or respiratory failure.
Symptoms of Atelectasis
- The symptoms of atelectasis depend on the extent of lung collapse and the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity, is a common symptom of atelectasis.
- Rapid Breathing: The body may compensate for reduced oxygen levels by increasing the breathing rate.
- Cough: A persistent cough, sometimes with mucus, may occur as the body tries to clear the airways.
- Chest Pain: Pain or discomfort in the chest, particularly on the side of the affected lung, may be present.
- Low Oxygen Levels: In severe cases, atelectasis can lead to low oxygen levels in the blood, causing symptoms such as bluish skin (cyanosis) or confusion.
- Fever: If atelectasis is caused by an infection, fever may also be present. In mild cases, atelectasis may not cause noticeable symptoms and may resolve on its own. However, if symptoms are severe or persistent, medical attention is necessary to prevent complications.
Causes of Atelectasis
- Atelectasis can result from a variety of factors that obstruct the airways or compress the lung tissue. Common causes include:
- Airway Obstruction: Blockages in the airways, often caused by mucus plugs, foreign objects, or tumors, can prevent air from reaching the alveoli, leading to their collapse.
- Post-Surgical Complications: Atelectasis is a common complication after surgery, particularly chest or abdominal surgery, due to restricted breathing, the effects of anesthesia, or pain that limits deep breathing.
- Lung Infections: Conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis can cause inflammation and mucus buildup, leading to airway blockages and atelectasis.
- Pressure on the Lung: External pressure from tumors, fluid buildup (pleural effusion), or enlarged lymph nodes can compress the lung and cause it to collapse.
- Inhaled Foreign Objects: In children, inhaling small objects like peanuts or toys can block the airways and cause atelectasis.
- Chronic Lung Conditions: Diseases such as cystic fibrosis, asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can increase the risk of atelectasis.
- Prolonged Bed Rest: Immobility can lead to shallow breathing, which reduces airflow to the lungs and increases the risk of atelectasis. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for determining the appropriate treatment approach.
Risk Factors of Atelectasis
- Several factors can increase the risk of developing atelectasis:
- Surgery: Individuals who undergo chest or abdominal surgery are at higher risk due to restricted breathing and the effects of anesthesia.
- Chronic Lung Conditions: Conditions such as asthma, COPD, or cystic fibrosis can increase the risk of airway blockages and atelectasis.
- Immobility: Prolonged bed rest or immobility can lead to shallow breathing, reducing airflow to the lungs.
- Age: Older adults and young children are more susceptible to atelectasis due to weaker lung function or smaller airways.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the lungs and increases the risk of mucus buildup and airway blockages.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put pressure on the lungs and diaphragm, making it harder to breathe deeply.
- Respiratory Infections: Conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis can increase the risk of atelectasis.
- Foreign Object Inhalation: Children are at higher risk of inhaling small objects, which can block the airways. Understanding these risk factors can help identify individuals at higher risk and encourage preventive measures.
Prevention of Atelectasis
- Preventing atelectasis involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and good respiratory practices:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: After surgery or during prolonged bed rest, deep breathing exercises can help keep the lungs inflated.
- Incentive Spirometry: Using a device to encourage deep breathing can prevent lung collapse.
- Mobility: Moving around as soon as possible after surgery or illness can improve lung function.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can improve lung health and reduce the risk of mucus buildup.
- Treating Infections: Promptly treating respiratory infections can prevent complications like atelectasis.
- Chest Physiotherapy: Techniques like clapping or vibration on the chest can help clear mucus and improve airflow.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated can help thin mucus and make it easier to clear from the airways.
- Vaccinations: Vaccines for influenza and pneumonia can reduce the risk of infections that may lead to atelectasis. Public health initiatives that promote awareness and education about atelectasis can also help reduce the burden of this condition.
Prognosis of Atelectasis
- The prognosis for atelectasis varies depending on the cause, severity, and timeliness of treatment:
- With Early Treatment: Most individuals with atelectasis recover fully with appropriate treatment, especially if the condition is detected early.
- Severe Cases: Severe or untreated atelectasis can lead to complications such as pneumonia, respiratory failure, or permanent lung damage.
- Recovery Time: Recovery can take several days to weeks, depending on the extent of lung collapse and the underlying cause.
- Preventive Measures: Deep breathing exercises, mobility, and treating underlying conditions can improve outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Chronic Conditions: Individuals with chronic lung diseases may require ongoing management to prevent recurrent atelectasis. Regular follow-up care and adherence to treatment plans are essential for managing atelectasis effectively.
Complications of Atelectasis
- If left untreated or poorly managed, atelectasis can lead to several complications:
- Pneumonia: Collapsed lung tissue is more susceptible to infections, increasing the risk of pneumonia.
- Respiratory Failure: Severe atelectasis can impair the lungs’ ability to provide oxygen to the body, leading to respiratory failure.
- Hypoxemia: Low oxygen levels in the blood can cause symptoms such as confusion, fatigue, or cyanosis (bluish skin).
- Lung Scarring: Repeated episodes of atelectasis can lead to scarring and permanent lung damage.
- Sepsis: If an infection spreads to the bloodstream, it can lead to a life-threatening condition called sepsis.
- Chronic Lung Disease: Prolonged atelectasis can contribute to the development of chronic lung conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing these complications and improving outcomes.
Related Diseases of Atelectasis
- Atelectasis is often associated with other respiratory and systemic conditions:
- Pneumonia: Atelectasis can increase the risk of developing pneumonia due to collapsed lung tissue.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Individuals with COPD are at higher risk of atelectasis due to mucus buildup and airway blockages.
- Asthma: Asthma can increase the risk of atelectasis by causing airway inflammation and mucus production.
- Cystic Fibrosis: This genetic condition leads to thick mucus production, increasing the risk of airway blockages and atelectasis.
- Lung Cancer: Tumors can compress the lung or block airways, leading to atelectasis.
- Pleural Effusion: Fluid buildup around the lungs can compress lung tissue and cause atelectasis.
- Respiratory Infections: Conditions like bronchitis or pneumonia can lead to atelectasis. Understanding these related conditions is essential for providing comprehensive care and improving outcomes for individuals with atelectasis.
Treatment of Atelectasis
The treatment of atelectasis depends on the cause, severity, and overall health of the individual. Common treatment options include: 1. **Deep Breathing Exercises**: Techniques such as incentive spirometry or coughing exercises can help reopen collapsed lung tissue. 2. **Chest Physiotherapy**: Techniques like clapping or vibration on the chest can help loosen mucus and improve airflow. 3. **Bronchoscopy**: If a blockage is causing atelectasis, a bronchoscopy may be performed to remove the obstruction. 4. **Medications**: Bronchodilators or mucolytics may be prescribed to open the airways or thin mucus. 5. **Oxygen Therapy**: Individuals with low oxygen levels may require supplemental oxygen. 6. **Surgery**: In rare cases, surgery may be needed to remove tumors or other sources of external pressure on the lung. 7. **Treating Underlying Conditions**: Addressing infections, chronic lung diseases, or other underlying causes is essential for preventing recurrence. A personalized treatment plan, developed in collaboration with a healthcare provider, is essential for effective management.
Generics For Atelectasis
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Acetylcysteine
Acetylcysteine

Cefaclor
Cefaclor

Cefuroxime
Cefuroxime

Acetylcysteine
Acetylcysteine

Cefaclor
Cefaclor

Cefuroxime
Cefuroxime