Overview Of Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
Streptococcal pharyngitis, commonly known as strep throat, is an infection of the pharynx and tonsils caused by group A *Streptococcus* (GAS), specifically *Streptococcus pyogenes*. It is a highly contagious condition that primarily affects children aged 5 to 15 but can occur in individuals of any age. Strep throat is characterized by sudden onset of sore throat, pain during swallowing, and fever. Unlike viral pharyngitis, which often accompanies colds, strep throat typically does not cause cough or nasal congestion. If left untreated, it can lead to complications such as rheumatic fever, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, or peritonsillar abscess. Prompt diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are essential to prevent these complications and reduce transmission.
Symptoms of Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
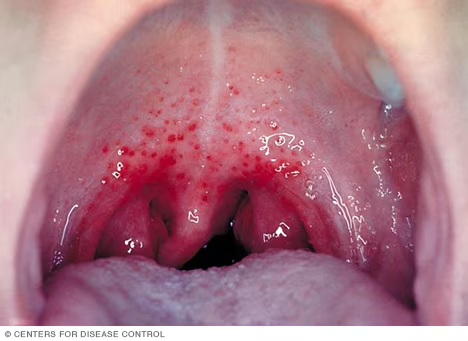
- The symptoms of streptococcal pharyngitis typically develop 2–5 days after exposure and include a sudden, severe sore throat, pain during swallowing, and fever (often above 101°F or 38.3°C). Patients may also experience headache, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, particularly in children. The tonsils and pharynx appear red and swollen, often with white or yellow patches of pus. Tender, swollen lymph nodes in the neck are common. Unlike viral pharyngitis, strep throat usually does not cause cough, runny nose, or hoarseness. A fine, red rash known as scarlet fever may develop in some cases, giving the skin a sandpaper-like texture. If untreated, symptoms may persist for 7–10 days, but complications can arise.
Causes of Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
- Streptococcal pharyngitis is caused by the bacterium *Streptococcus pyogenes*, a group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. The bacteria are transmitted through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, or through direct contact with contaminated surfaces. Crowded environments, such as schools or daycare centers, facilitate the spread of the infection. The bacteria colonize the pharynx and tonsils, triggering an inflammatory response that leads to the characteristic symptoms. While *Streptococcus pyogenes* is the primary cause, other streptococcal species, such as groups C and G, can occasionally cause similar symptoms. Risk factors include close contact with an infected individual, poor hygiene practices, and a weakened immune system.
Risk Factors of Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
- Several factors increase the risk of developing streptococcal pharyngitis. Children aged 5 to 15 are most susceptible due to their close contact in schools and daycare settings. Adults who live or work in crowded environments, such as military barracks or dormitories, are also at higher risk. Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing hands regularly or sharing utensils, can facilitate the spread of the bacteria. A weakened immune system, due to conditions like HIV or diabetes, or medications such as corticosteroids, increases susceptibility. Seasonal factors play a role, with strep throat being more common in late winter and early spring. A history of recurrent streptococcal infections or close contact with an infected individual further elevates the risk.
Prevention of Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
- Preventing streptococcal pharyngitis involves reducing exposure to the bacteria and practicing good hygiene. Regular handwashing with soap and water, especially after coughing or sneezing and before eating, is essential. Avoiding close contact with individuals who have strep throat and not sharing utensils, cups, or personal items can help prevent transmission. In households or settings with an infected individual, disinfecting commonly touched surfaces and encouraging the use of tissues or elbows to cover coughs and sneezes can reduce spread. For individuals with recurrent strep throat, identifying and treating asymptomatic carriers, such as family members, may be necessary. Vaccines for group A *Streptococcus* are under development but not yet available.
Prognosis of Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
- The prognosis for streptococcal pharyngitis is excellent with prompt diagnosis and appropriate antibiotic treatment. Most patients experience significant improvement within 24–48 hours of starting antibiotics, and symptoms typically resolve completely within a week. Early treatment reduces the risk of complications, such as rheumatic fever, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, or peritonsillar abscess. Without treatment, the infection can persist, and the risk of complications increases. Recurrent episodes of strep throat may occur, particularly in individuals with untreated close contacts or underlying risk factors. Long-term complications are rare but can have serious consequences, emphasizing the importance of timely and effective management.
Complications of Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
- If left untreated, streptococcal pharyngitis can lead to several complications. Rheumatic fever is a serious immune-mediated condition that can affect the heart, joints, skin, and brain, potentially causing permanent heart valve damage. Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis is a kidney disorder characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli, leading to hematuria, proteinuria, and hypertension. Local complications include peritonsillar abscess, a collection of pus around the tonsils that can cause severe pain, difficulty swallowing, and airway obstruction. Other rare complications include scarlet fever, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, and invasive infections such as bacteremia or necrotizing fasciitis. Prompt treatment with antibiotics significantly reduces the risk of these complications.
Related Diseases of Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
- Streptococcal pharyngitis is closely associated with several other conditions. Scarlet fever, caused by the same bacterium, presents with a characteristic rash and strawberry tongue. Rheumatic fever and post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis are immune-mediated complications that can occur weeks after an untreated or inadequately treated strep throat infection. Peritonsillar abscess, a localized complication, can develop if the infection spreads to the surrounding tissues. Other streptococcal infections, such as impetigo or cellulitis, may occur concurrently or independently. Viral pharyngitis, caused by pathogens like the Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis) or adenovirus, can mimic strep throat but requires different management. Understanding these related diseases is essential for accurate diagnosis and comprehensive treatment.
Treatment of Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
The primary treatment for streptococcal pharyngitis is antibiotics, which reduce the duration of symptoms, prevent complications, and decrease transmission. Penicillin or amoxicillin is the first-line therapy, typically administered for 10 days. For patients allergic to penicillin, alternatives include cephalosporins, macrolides (e.g., azithromycin), or clindamycin. Symptomatic relief can be achieved with analgesics like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce fever and throat pain. Gargling with warm salt water and staying hydrated are supportive measures. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics even if symptoms improve to prevent complications like rheumatic fever. Close contacts of the infected individual should be monitored for symptoms, and prophylactic treatment may be considered in certain cases.
Generics For Streptococcal pharyngitis&tonsillitis
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.