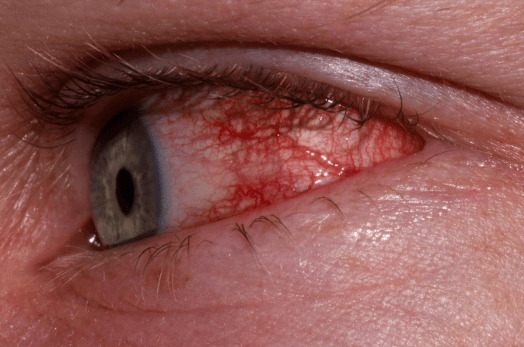
Overview Of Allergic conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is an inflammatory condition of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane covering the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids. It occurs when the eyes react to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold spores, triggering an immune response. This condition is a common ocular manifestation of allergies and can occur seasonally or year-round, depending on the allergen. Symptoms include redness, itching, tearing, and swelling of the eyes, which can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Allergic conjunctivitis is not contagious and is typically associated with other allergic conditions like allergic rhinitis or asthma. It is classified into several subtypes, including seasonal allergic conjunctivitis (SAC), perennial allergic conjunctivitis (PAC), and more severe forms like vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) and atopic keratoconjunctivitis (AKC).
Symptoms of Allergic conjunctivitis
- The symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis are primarily ocular and include redness, itching, tearing, and a burning or gritty sensation in the eyes. The eyelids may become swollen, and the conjunctiva can appear puffy or inflamed. In severe cases, individuals may experience photophobia (sensitivity to light) or blurred vision. Stringy or watery discharge is common, and rubbing the eyes can worsen symptoms. Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis (SAC) symptoms are often more intense during specific times of the year, while perennial allergic conjunctivitis (PAC) symptoms may be milder but persistent. Severe forms like vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) and atopic keratoconjunctivitis (AKC) can cause additional complications, such as corneal ulcers or scarring.
Causes of Allergic conjunctivitis
- The primary cause of allergic conjunctivitis is an exaggerated immune response to airborne allergens. When the eyes come into contact with allergens such as pollen, dust mites, animal dander, or mold spores, mast cells in the conjunctiva release histamine and other inflammatory mediators. This leads to the characteristic symptoms of redness, itching, and swelling. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as individuals with a family history of allergies are more likely to develop the condition. Environmental factors, such as pollution and exposure to irritants like smoke or strong odors, can exacerbate symptoms. In some cases, contact lens use or eye cosmetics may contribute to allergic conjunctivitis by introducing allergens or irritants to the eye surface.
Risk Factors of Allergic conjunctivitis
- Several factors increase the risk of developing allergic conjunctivitis. A personal or family history of allergies, asthma, or eczema is a significant risk factor, as these conditions share common immune pathways. Exposure to environmental allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, is another major contributor. Living in urban areas with high levels of air pollution or working in occupations with frequent allergen exposure can also elevate the risk. Contact lens wearers are more susceptible due to the potential for allergen accumulation on the lenses. Additionally, individuals with compromised ocular surfaces, such as those with dry eye syndrome, may be more prone to allergic conjunctivitis. Age can also play a role, with children and young adults being more commonly affected.
Prevention of Allergic conjunctivitis
- Preventing allergic conjunctivitis involves minimizing exposure to known allergens and adopting strategies to reduce immune system sensitivity. For seasonal allergies, monitoring pollen counts and staying indoors during peak pollen times can help. Using air purifiers with HEPA filters and keeping windows closed can reduce indoor allergen exposure. Regularly washing bedding in hot water and using allergen-proof covers can minimize dust mite exposure. For individuals with pet allergies, limiting contact with animals or designating pet-free zones in the home may be beneficial. Avoiding eye rubbing and practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, can prevent the introduction of allergens or irritants to the eyes. Wearing sunglasses outdoors can provide a barrier against airborne allergens.
Prognosis of Allergic conjunctivitis
- The prognosis for allergic conjunctivitis is generally favorable, as the condition is manageable with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. Most individuals experience significant symptom relief with the use of antihistamine eye drops and allergen avoidance. However, allergic conjunctivitis is a chronic condition, and symptoms may recur with ongoing exposure to allergens. Severe forms like vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) and atopic keratoconjunctivitis (AKC) may require more aggressive treatment and have a higher risk of complications, such as corneal scarring or vision impairment. Early diagnosis and consistent management are crucial for improving quality of life and preventing long-term complications.
Complications of Allergic conjunctivitis
- If left untreated, allergic conjunctivitis can lead to several complications. Chronic inflammation of the conjunctiva can result in conjunctival scarring or the formation of papillae (small bumps) on the inner eyelids. Severe forms of the condition, such as vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) and atopic keratoconjunctivitis (AKC), can cause corneal ulcers, thinning, or scarring, potentially leading to vision loss. Persistent rubbing of the eyes due to itching can exacerbate inflammation and increase the risk of secondary infections. Additionally, the chronic discomfort and visual disturbances associated with allergic conjunctivitis can impact daily activities, sleep quality, and overall well-being, leading to reduced productivity and emotional distress.
Related Diseases of Allergic conjunctivitis
- Allergic conjunctivitis is closely associated with other allergic and inflammatory conditions. It is often seen in conjunction with allergic rhinitis (hay fever), as both conditions are triggered by similar allergens and share common immune pathways. Asthma and atopic dermatitis (eczema) are also frequently linked to allergic conjunctivitis, particularly in individuals with a genetic predisposition to atopy. Severe forms of allergic conjunctivitis, such as vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) and atopic keratoconjunctivitis (AKC), are associated with more systemic allergic conditions and may coexist with keratoconus, a corneal thinning disorder. Additionally, dry eye syndrome and blepharitis are common comorbidities that can exacerbate symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis. Understanding these related diseases is essential for comprehensive management and treatment.
Treatment of Allergic conjunctivitis
The treatment of allergic conjunctivitis focuses on relieving symptoms and reducing exposure to allergens. Artificial tears and cold compresses can provide immediate relief from itching and discomfort. Antihistamine eye drops, such as olopatadine or ketotifen, are commonly used to block the effects of histamine and alleviate symptoms. Mast cell stabilizers, such as cromolyn sodium, can prevent the release of inflammatory mediators and are particularly useful for long-term management. In severe cases, corticosteroid eye drops may be prescribed, but their use is typically limited due to potential side effects. Oral antihistamines can help control systemic allergy symptoms but may cause dry eyes. Allergen avoidance measures, such as using air purifiers and avoiding outdoor activities during high pollen counts, are essential for managing the condition.
Generics For Allergic conjunctivitis
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Bepotastine Besilate 1.5% Eye prep
Bepotastine Besilate 1.5% Eye prep

Chloramphenicol 0.5% + Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye&Ear drop
Chloramphenicol 0.5% + Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye&Ear drop

Dexamethasone 0.05% Eye prep
Dexamethasone 0.05% Eye prep

Dexamethasone 0.1% E&E prep
Dexamethasone 0.1% E&E prep

Dexamethasone 0.1% + Gatifloxacin 0.3%
Dexamethasone 0.1% + Gatifloxacin 0.3%

Diclofenac Sodium 0.1% Eye prep
Diclofenac Sodium 0.1% Eye prep

Epinastine Hydrochloride 0.05% Eye prep
Epinastine Hydrochloride 0.05% Eye prep

Gentamicin 0.3% + Hydrocortisone Acetate 1% Eye prep
Gentamicin 0.3% + Hydrocortisone Acetate 1% Eye prep

Ketorolac Tromethamine 0.5% Eye prep
Ketorolac Tromethamine 0.5% Eye prep

Ketotifen
Ketotifen

Ketotifen Eye prep
Ketotifen Eye prep

Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3% Eye prep
Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3% Eye prep

Methylprednisolone Sodium Succinate
Methylprednisolone Sodium Succinate

Olopatadine 0.2% Eye prep
Olopatadine 0.2% Eye prep

Pemirolast Potassium 0.1% Eye prep
Pemirolast Potassium 0.1% Eye prep

Pheniramine Maleate
Pheniramine Maleate

Prednisolone 1% Eye prep
Prednisolone 1% Eye prep

Rupatadine
Rupatadine

Sodium Cromoglycate 2% Eye&Nasal prep
Sodium Cromoglycate 2% Eye&Nasal prep

Sodium Cromoglycate 4% Eye&Nasal prep
Sodium Cromoglycate 4% Eye&Nasal prep

Lodoxamide
Lodoxamide

Pheniramine Maleate + Naphazoline HCl Eye prep
Pheniramine Maleate + Naphazoline HCl Eye prep

Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye prep
Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye prep

Alcaftadine
Alcaftadine

Bepotastine Besilate 1.5% Eye prep
Bepotastine Besilate 1.5% Eye prep

Chloramphenicol 0.5% + Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye&Ear drop
Chloramphenicol 0.5% + Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye&Ear drop

Dexamethasone 0.05% Eye prep
Dexamethasone 0.05% Eye prep

Dexamethasone 0.1% E&E prep
Dexamethasone 0.1% E&E prep

Dexamethasone 0.1% + Gatifloxacin 0.3%
Dexamethasone 0.1% + Gatifloxacin 0.3%

Diclofenac Sodium 0.1% Eye prep
Diclofenac Sodium 0.1% Eye prep

Epinastine Hydrochloride 0.05% Eye prep
Epinastine Hydrochloride 0.05% Eye prep

Gentamicin 0.3% + Hydrocortisone Acetate 1% Eye prep
Gentamicin 0.3% + Hydrocortisone Acetate 1% Eye prep

Ketorolac Tromethamine 0.5% Eye prep
Ketorolac Tromethamine 0.5% Eye prep

Ketotifen
Ketotifen

Ketotifen Eye prep
Ketotifen Eye prep

Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3% Eye prep
Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3% Eye prep

Methylprednisolone Sodium Succinate
Methylprednisolone Sodium Succinate

Olopatadine 0.2% Eye prep
Olopatadine 0.2% Eye prep

Pemirolast Potassium 0.1% Eye prep
Pemirolast Potassium 0.1% Eye prep

Pheniramine Maleate
Pheniramine Maleate

Prednisolone 1% Eye prep
Prednisolone 1% Eye prep

Rupatadine
Rupatadine

Sodium Cromoglycate 2% Eye&Nasal prep
Sodium Cromoglycate 2% Eye&Nasal prep

Sodium Cromoglycate 4% Eye&Nasal prep
Sodium Cromoglycate 4% Eye&Nasal prep

Lodoxamide
Lodoxamide

Pheniramine Maleate + Naphazoline HCl Eye prep
Pheniramine Maleate + Naphazoline HCl Eye prep

Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye prep
Dexamethasone 0.1% Eye prep

Alcaftadine
Alcaftadine