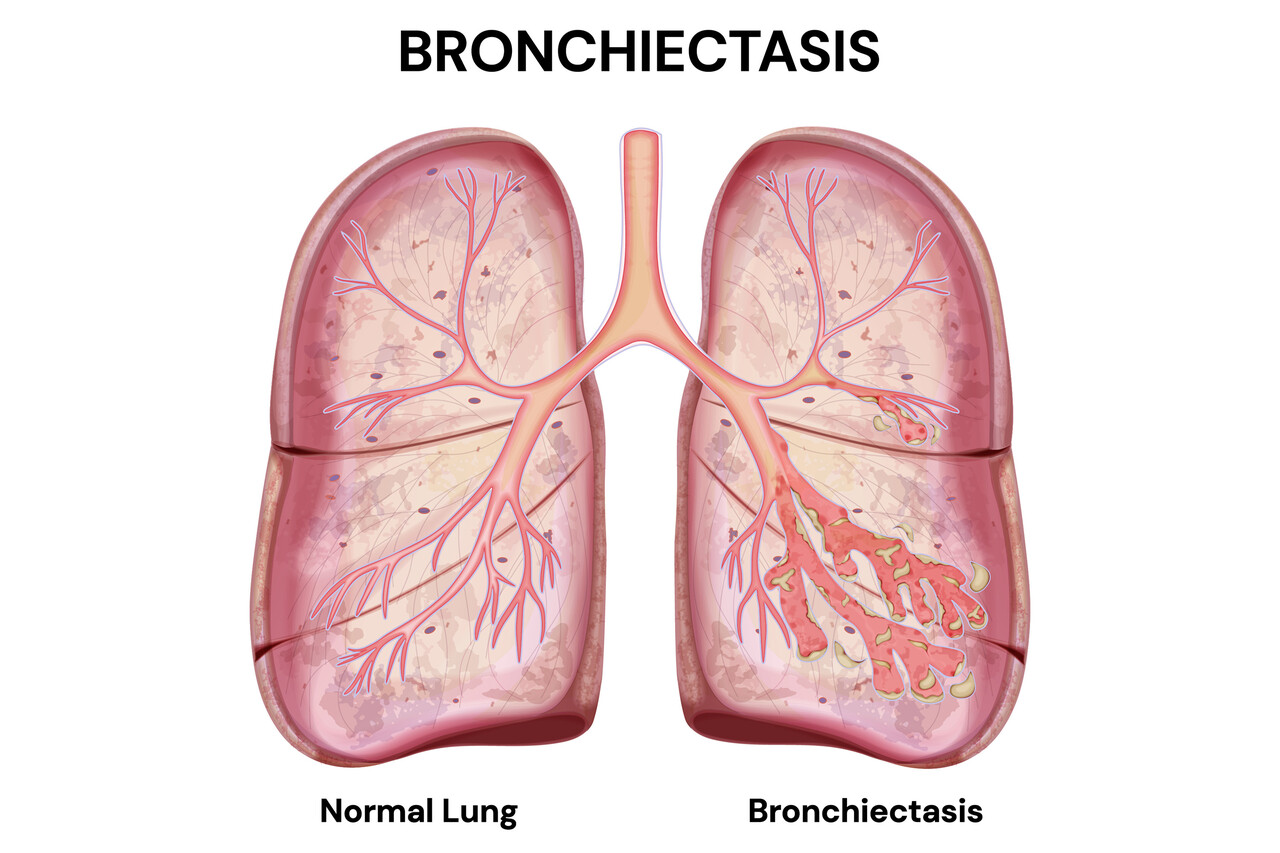
Overview Of Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a chronic condition characterized by abnormal widening of the airways in the lungs, leading to mucus build-up and recurrent infections. This can result in irreversible lung damage and impaired lung function.
Symptoms of Bronchiectasis
- - Persistent cough with thick mucus production. - Recurrent lung infections. - Wheezing or shortness of breath. - Chest pain or discomfort. - Fatigue and general malaise.
Causes of Bronchiectasis
- The primary causes of bronchiectasis include: - Chronic infections: Recurrent bacterial, viral, or fungal lung infections can damage airway walls. - Cystic fibrosis: A genetic disorder causing thick, sticky mucus, often leading to bronchiectasis. - Immune system disorders: Conditions like common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) or HIV. - Autoimmune diseases: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or Sjögren's syndrome can increase the risk. - Foreign body aspiration: Inhalation of objects or substances that damage the airways. - Congenital abnormalities: Structural lung defects present at birth.
Risk Factors of Bronchiectasis
- - Cystic fibrosis: The most common risk factor in children and young adults. - History of lung infections: Including pneumonia, tuberculosis, or whooping cough. - Exposure to environmental toxins: Prolonged exposure to harmful substances like smoke or pollution. - Immunodeficiency: Conditions that weaken the immune system. - Genetic predisposition: Family history of lung diseases.
Prevention of Bronchiectasis
- - Vaccination: Regular vaccines for flu, pneumonia, and other respiratory infections. - Early treatment: Prompt management of respiratory infections. - Smoking cessation: To prevent airway damage. - Airway clearance exercises: For those with chronic conditions.
Prognosis of Bronchiectasis
- With appropriate management, many individuals can maintain a good quality of life. However, untreated or severe cases can lead to respiratory failure or chronic lung infections.
Complications of Bronchiectasis
- - Recurrent lung infections. - Respiratory failure. - Hemoptysis (coughing up blood). - Cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure). - Progressive lung damage.
Related Diseases of Bronchiectasis
- - Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). - Asthma. - Pulmonary fibrosis. - Tuberculosis. - Cystic fibrosis.
Treatment of Bronchiectasis
- **Airway clearance techniques**: Physical therapy and devices to help clear mucus. - **Antibiotics**: To treat and prevent lung infections. - **Bronchodilators**: Medications to open airways and improve breathing. - **Anti-inflammatory medications**: To reduce inflammation in the airways. - **Surgery**: In severe cases, resection of damaged lung areas.
Generics For Bronchiectasis
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Acetylcysteine
Acetylcysteine

Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin

Azithromycin
Azithromycin

Carbocisteine
Carbocisteine

Gentamicin
Gentamicin

Sulphamethoxazole + Trimethoprim (Co-trimoxazole)
Sulphamethoxazole + Trimethoprim (Co-trimoxazole)

Tetracycline Hydrochloride
Tetracycline Hydrochloride

Clarithromycin
Clarithromycin

Acetylcysteine
Acetylcysteine

Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin

Azithromycin
Azithromycin

Carbocisteine
Carbocisteine

Gentamicin
Gentamicin

Sulphamethoxazole + Trimethoprim (Co-trimoxazole)
Sulphamethoxazole + Trimethoprim (Co-trimoxazole)

Tetracycline Hydrochloride
Tetracycline Hydrochloride

Clarithromycin
Clarithromycin