Overview Of Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light is essential for maintaining skin health and preventing long-term consequences such as premature aging, sunburn, and skin cancer. UV radiation, which comes from the sun and artificial sources like tanning beds, is classified into UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, causing premature aging and wrinkles, while UVB rays primarily affect the outer layers, leading to sunburn and direct DNA damage. Prolonged or excessive exposure to UV light can result in photoaging, hyperpigmentation, and an increased risk of skin cancers, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Protective measures, such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours, are critical for minimizing UV-induced skin damage. Public health initiatives and education play a vital role in promoting sun safety and skin cancer prevention.
Symptoms of Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
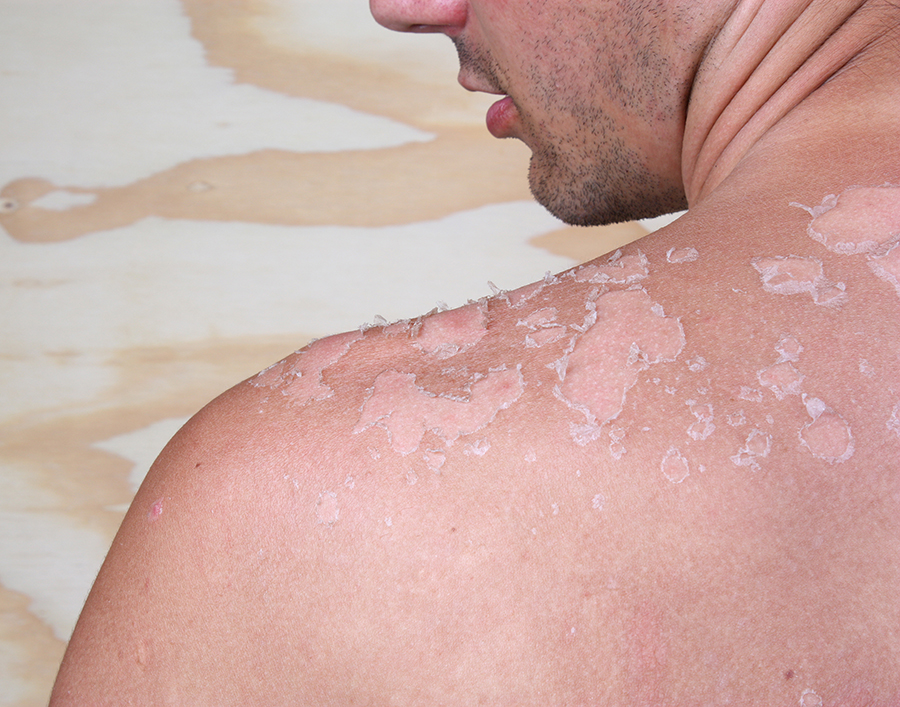
- The symptoms of UV-induced skin damage vary depending on the extent and duration of exposure. Acute symptoms include sunburn, characterized by redness, pain, swelling, and blistering. Long-term exposure can lead to photoaging, which manifests as wrinkles, fine lines, leathery texture, and loss of elasticity. Hyperpigmentation, such as age spots or melasma, may also develop due to UV exposure. In severe cases, UV damage can result in actinic keratoses, which are precancerous skin lesions, or skin cancers such as melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Recognizing these symptoms and taking preventive measures are crucial for minimizing UV-induced skin damage.
Causes of Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
- Skin damage from UV light is caused by prolonged or excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. UVA rays, which make up the majority of UV radiation reaching the Earth's surface, penetrate deep into the skin and contribute to premature aging, wrinkles, and suppression of the immune system. UVB rays, though less prevalent, are more intense and directly damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to sunburn and an increased risk of skin cancer. Factors such as geographic location, altitude, time of day, and skin type influence the extent of UV exposure and damage. Understanding these causes is essential for developing effective strategies to protect the skin from UV radiation.
Risk Factors of Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
- Several factors increase the risk of UV-induced skin damage. Fair skin, which has less melanin, provides less natural protection against UV radiation. Geographic location and altitude influence UV intensity, with higher levels near the equator and at higher elevations. Prolonged outdoor activities, especially during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), increase exposure. The use of tanning beds or lamps significantly elevates the risk of skin damage and cancer. A history of sunburns, particularly during childhood, increases the likelihood of long-term damage. Understanding these risk factors is essential for targeted prevention and intervention. Public health initiatives, such as education and access to protective measures, play a critical role in reducing UV-induced skin damage.
Prevention of Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
- Preventing UV-induced skin damage involves a combination of protective measures and lifestyle changes. Using broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, reapplying every two hours, and after swimming or sweating, is essential. Wearing protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, long sleeves, and sunglasses, can shield the skin from UV rays. Seeking shade, especially during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), reduces direct exposure. Avoiding tanning beds and lamps is critical for preventing artificial UV damage. Regular skin checks and self-examinations help detect early signs of damage or skin cancer. Public health initiatives, such as education and access to sunscreen, play a critical role in promoting sun safety and preventing UV-induced skin damage.
Prognosis of Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
- The prognosis for UV-induced skin damage varies depending on the extent of damage and the timeliness of intervention. Early detection and treatment of sunburn and photoaging can improve skin appearance and prevent further damage. However, long-term UV exposure can lead to irreversible changes, such as deep wrinkles and loss of elasticity. The prognosis for skin cancer depends on the type and stage at diagnosis, with early detection associated with better outcomes. Regular skin checks, sun protection, and adherence to treatment plans are essential for maintaining skin health. Public health initiatives, such as education and access to dermatological care, play a critical role in improving prognosis and reducing the burden of UV-induced skin damage.
Complications of Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
- UV-induced skin damage can lead to several complications, both immediate and long-term. Acute complications include severe sunburn, which can cause pain, blistering, and secondary infections. Long-term complications include photoaging, characterized by wrinkles, sagging, and uneven skin tone. Hyperpigmentation, such as age spots or melasma, can affect appearance and self-esteem. The most serious complication is skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, which can be life-threatening if not detected and treated early. Addressing these complications requires a comprehensive approach, including sun protection, regular skin checks, and timely medical intervention. Early intervention is crucial for minimizing the impact of UV-induced skin damage.
Related Diseases of Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
- UV-induced skin damage is closely associated with several related conditions and diseases. Photoaging, characterized by wrinkles, fine lines, and loss of elasticity, is a direct result of chronic UV exposure. Hyperpigmentation, such as age spots and melasma, can also result from UV damage. Actinic keratoses, which are precancerous lesions, are linked to long-term sun exposure. Skin cancers, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, are the most serious consequences of UV damage. Additionally, UV exposure can exacerbate other skin conditions, such as lupus or rosacea. Recognizing these related diseases is essential for comprehensive care and effective management of UV-induced skin damage. Public health initiatives, such as education and access to dermatological care, play a critical role in reducing the burden of UV-related skin conditions.
Treatment of Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
The treatment of UV-induced skin damage depends on the extent and type of damage. For sunburn, cooling measures such as cold compresses, aloe vera, and over-the-counter pain relievers can alleviate symptoms. Moisturizers and topical antioxidants may help repair the skin barrier and reduce inflammation. Photoaging can be addressed with retinoids, chemical peels, or laser treatments to improve skin texture and reduce wrinkles. Hyperpigmentation may be treated with topical lightening agents, such as hydroquinone or vitamin C, or procedures like microdermabrasion. Precancerous lesions, such as actinic keratoses, may require cryotherapy, topical treatments, or photodynamic therapy. Skin cancers are treated with surgical excision, radiation, or other targeted therapies. Treatment plans should be individualized based on the patient's specific needs and skin condition.
Generics For Reducing skin damage from ultraviolet (UV) light
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin

Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin