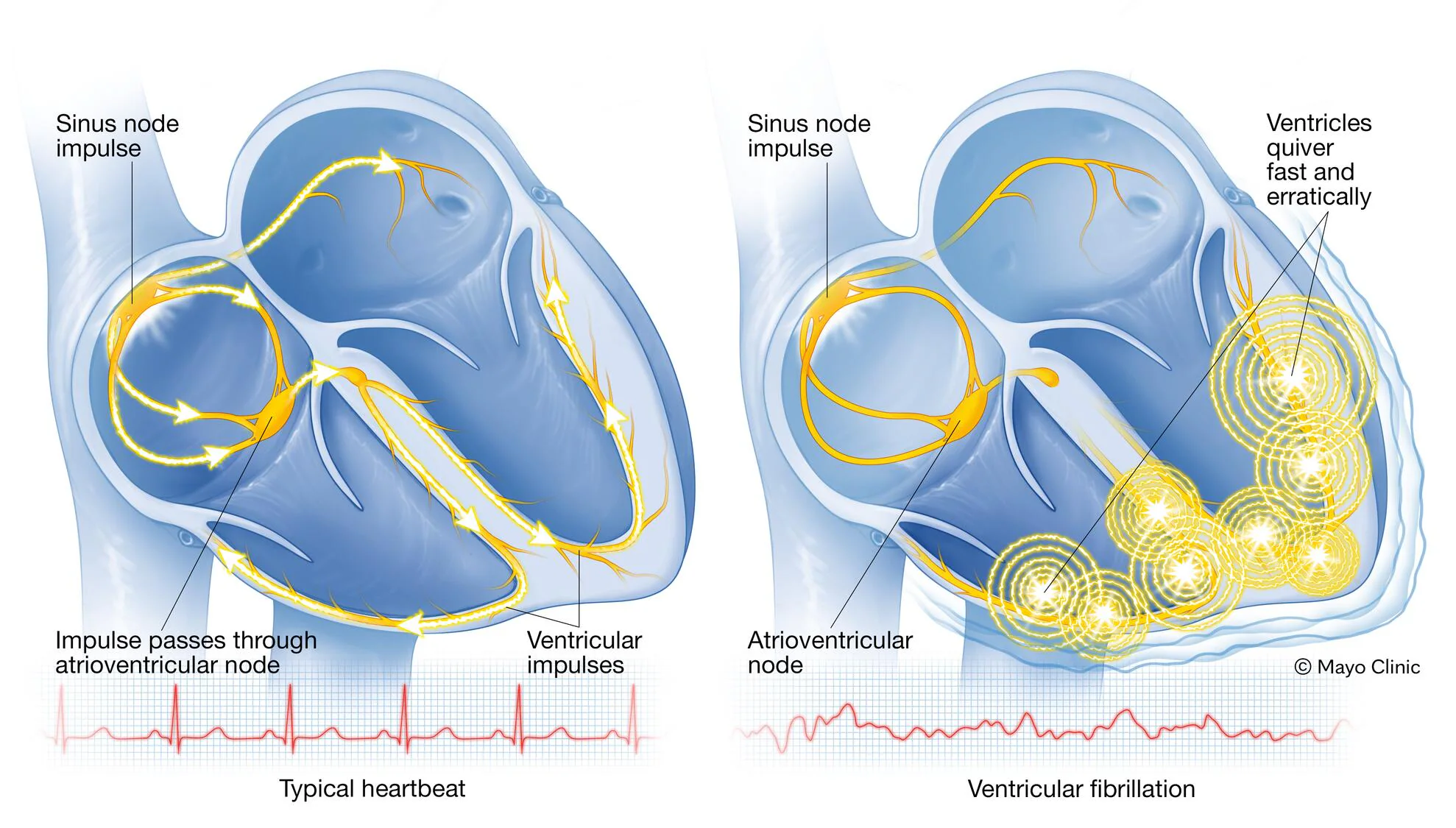
Overview Of Ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia characterized by rapid, chaotic electrical activity in the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart. This disorganized activity prevents the heart from pumping blood effectively, leading to sudden cardiac arrest and death if not treated immediately. VF is a medical emergency that requires prompt defibrillation to restore a normal heart rhythm. It is often associated with underlying heart disease, such as myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, or electrolyte imbalances. Early recognition and intervention are critical for survival. ---
Symptoms of Ventricular fibrillation
- Ventricular fibrillation (VF) causes sudden loss of effective cardiac output, leading to immediate symptoms such as loss of consciousness, absence of pulse, and cessation of breathing. There are no warning signs or prodromal symptoms, making VF a sudden and catastrophic event. If not treated within minutes, VF results in death due to lack of blood flow to vital organs. Early recognition of cardiac arrest and prompt initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation are crucial for survival. ---
Causes of Ventricular fibrillation
- Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is caused by abnormal electrical activity in the ventricles, often triggered by underlying heart conditions. The most common cause is ischemic heart disease, particularly acute myocardial infarction, which disrupts the heart’s electrical system. Other causes include cardiomyopathy, heart failure, electrolyte imbalances (e.g., hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia), drug toxicity (e.g., from antiarrhythmics or stimulants), and genetic conditions like long QT syndrome or Brugada syndrome. Trauma, electric shock, or severe hypoxia can also precipitate VF. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for prevention and management. ---
Risk Factors of Ventricular fibrillation
- Several factors increase the risk of ventricular fibrillation (VF). The most significant risk factor is underlying heart disease, particularly coronary artery disease and prior myocardial infarction. Other risk factors include cardiomyopathy, heart failure, electrolyte imbalances, and genetic arrhythmia syndromes like long QT syndrome or Brugada syndrome. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, excessive alcohol use, or stimulant abuse, also elevate the risk. Preventive measures, such as managing heart disease and avoiding triggers, reduce the likelihood of VF. ---
Prevention of Ventricular fibrillation
- Preventing ventricular fibrillation (VF) involves managing underlying risk factors and adopting heart-healthy lifestyles. Controlling conditions like coronary artery disease, hypertension, and diabetes reduces the risk. Avoiding excessive alcohol or stimulant use and maintaining electrolyte balance are important. For high-risk patients, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) provide protection against life-threatening arrhythmias. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers ensures early detection and management of risk factors. ---
Prognosis of Ventricular fibrillation
- The prognosis for ventricular fibrillation (VF) depends on the timeliness of intervention. Immediate defibrillation and CPR significantly improve survival rates, but delays in treatment drastically reduce the chances of survival. Survivors of VF are at high risk of recurrence and require long-term management, including ICD implantation and treatment of underlying heart disease. Early recognition, prompt treatment, and adherence to preventive measures improve outcomes and reduce mortality. ---
Complications of Ventricular fibrillation
- Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is a life-threatening condition that, if not treated immediately, leads to sudden cardiac death. Even with successful resuscitation, survivors may experience complications such as brain injury due to prolonged lack of oxygen (anoxic brain injury). Long-term complications include heart failure, recurrent arrhythmias, or psychological trauma. Early intervention and proper management are essential to prevent complications and ensure patient safety. ---
Related Diseases of Ventricular fibrillation
- Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is closely related to other cardiac arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia (VT) or atrial fibrillation (AF). It shares similarities with conditions like myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, and heart failure, which are common underlying causes of VF. Genetic arrhythmia syndromes, such as long QT syndrome or Brugada syndrome, are also associated with VF. Understanding these related diseases is important for comprehensive diagnosis and management. Preventive measures for VF also reduce the risk of other cardiovascular conditions. ---
Treatment of Ventricular fibrillation
The treatment of ventricular fibrillation (VF) is a medical emergency requiring immediate action. The first step is to initiate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to maintain blood flow to vital organs. Defibrillation, using an automated external defibrillator (AED) or manual defibrillator, is the definitive treatment to restore a normal heart rhythm. Advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) protocols, including administration of epinephrine and antiarrhythmic medications (e.g., amiodarone), are used if initial defibrillation attempts fail. Long-term management includes implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) to prevent recurrence and treatment of underlying conditions. ---
Generics For Ventricular fibrillation
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Amiodarone Hydrochloride
Amiodarone Hydrochloride

Dextrose + Lidocaine Hydrochloride
Dextrose + Lidocaine Hydrochloride

Amiodarone Hydrochloride
Amiodarone Hydrochloride

Dextrose + Lidocaine Hydrochloride
Dextrose + Lidocaine Hydrochloride