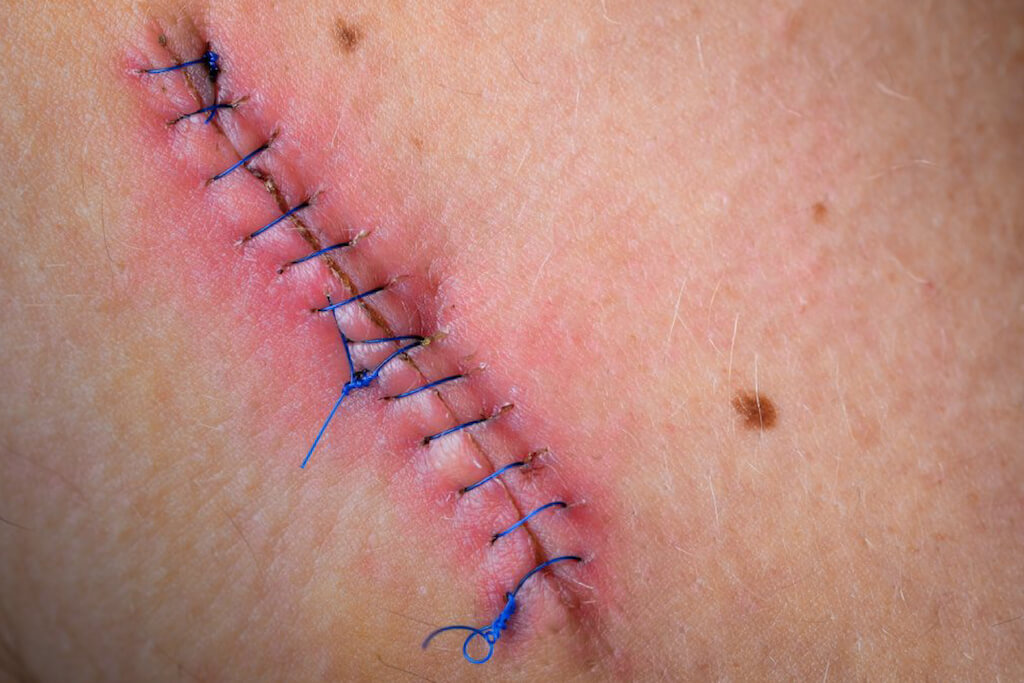
Overview Of Postoperative infections
Postoperative infections are infections that occur after a surgical procedure. They can affect the surgical site or spread to deeper parts of the body. These infections arise due to bacterial or other pathogenic entry into the body during or after the procedure. Symptoms may include fever, redness, swelling, increased pain at the site, and discharge. Risk factors vary from the surgical environment to the patient’s health condition and aftercare.
Symptoms of Postoperative infections
- - Localized symptoms: Redness, swelling, warmth, and pain around the surgical site. - Systemic symptoms: Fever, chills, and feeling unwell. - Discharge: The presence of pus or foul-smelling fluids. - Wound healing delay: Slower recovery at the incision site due to infection.
Causes of Postoperative infections
- The primary cause of postoperative infections is the introduction of pathogens during or after surgery. - Surgical technique: Inadequate aseptic technique or contamination can introduce bacteria. - Patient health: Weakened immune systems, diabetes, or obesity increase vulnerability. - Inadequate wound care: Poor hygiene or failure to clean and dress the wound can lead to infections. - Contaminated instruments/environment: If instruments are not properly sterilized, infection risks rise.
Risk Factors of Postoperative infections
- Several factors increase the risk of postoperative infections: - Surgical procedure: Complex or invasive surgeries have higher infection risks. - Immune status: Weakened immune systems due to conditions like cancer or diabetes make individuals more susceptible. - Obesity: Excess body fat can impair wound healing and promote infection. - Inadequate wound care: Improper care of the wound after surgery can invite infection. - Age: Elderly individuals have a higher infection risk due to less efficient immune responses.
Prevention of Postoperative infections
- Preventing postoperative infections involves: - Proper aseptic technique: Ensuring sterile conditions during surgery. - Antibiotic prophylaxis: Administering antibiotics before, during, and after surgery to prevent infection. - Wound care: Following proper procedures for cleaning and dressing the surgical site. - Patient management: Control of underlying conditions like diabetes and smoking cessation to promote healing.
Prognosis of Postoperative infections
- The prognosis is generally favorable if the infection is detected early and treated appropriately. Early treatment of mild infections with antibiotics and proper wound care often leads to full recovery. In severe cases or if the infection spreads, complications can arise, leading to prolonged hospital stays or additional surgeries. The patient's overall health significantly influences recovery outcomes.
Complications of Postoperative infections
- Complications of postoperative infections can include: - Sepsis: A systemic infection that affects multiple organs and can be life-threatening. - Chronic infection: A long-lasting infection that hinders recovery and may lead to more severe conditions. - Abscess formation: Pockets of pus that may need to be drained. - Prolonged hospitalization: Severe infections may require extended stays in the hospital for treatment and monitoring.
Related Diseases of Postoperative infections
- Postoperative infections are related to: - Sepsis: A widespread infection that can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly. - Abscesses: Localized pockets of infection that require drainage. - Deep tissue infections: Infections that extend beyond the surface and affect deeper body parts like organs. - Chronic wounds: Infections that prevent proper healing and can lead to ongoing health problems.
Treatment of Postoperative infections
Postoperative infections are treated with: - **Antibiotics**: Prescribed based on the specific pathogen identified in cultures. - **Wound care**: Regular cleaning, dressing, and monitoring of the surgical site. - **Surgical drainage**: In cases of abscess formation, draining fluid from the infection site may be necessary. - **Surgical revision**: If necessary, further surgery might be required to remove infected tissue.
Generics For Postoperative infections
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Amikacin
Amikacin

Cefotaxime
Cefotaxime

Cefoxitin
Cefoxitin

Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone

Imipenem + Cilastatin
Imipenem + Cilastatin

Meropenem
Meropenem

Piperacillin + Tazobactam
Piperacillin + Tazobactam

Amikacin
Amikacin

Cefotaxime
Cefotaxime

Cefoxitin
Cefoxitin

Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone

Imipenem + Cilastatin
Imipenem + Cilastatin

Meropenem
Meropenem

Piperacillin + Tazobactam
Piperacillin + Tazobactam