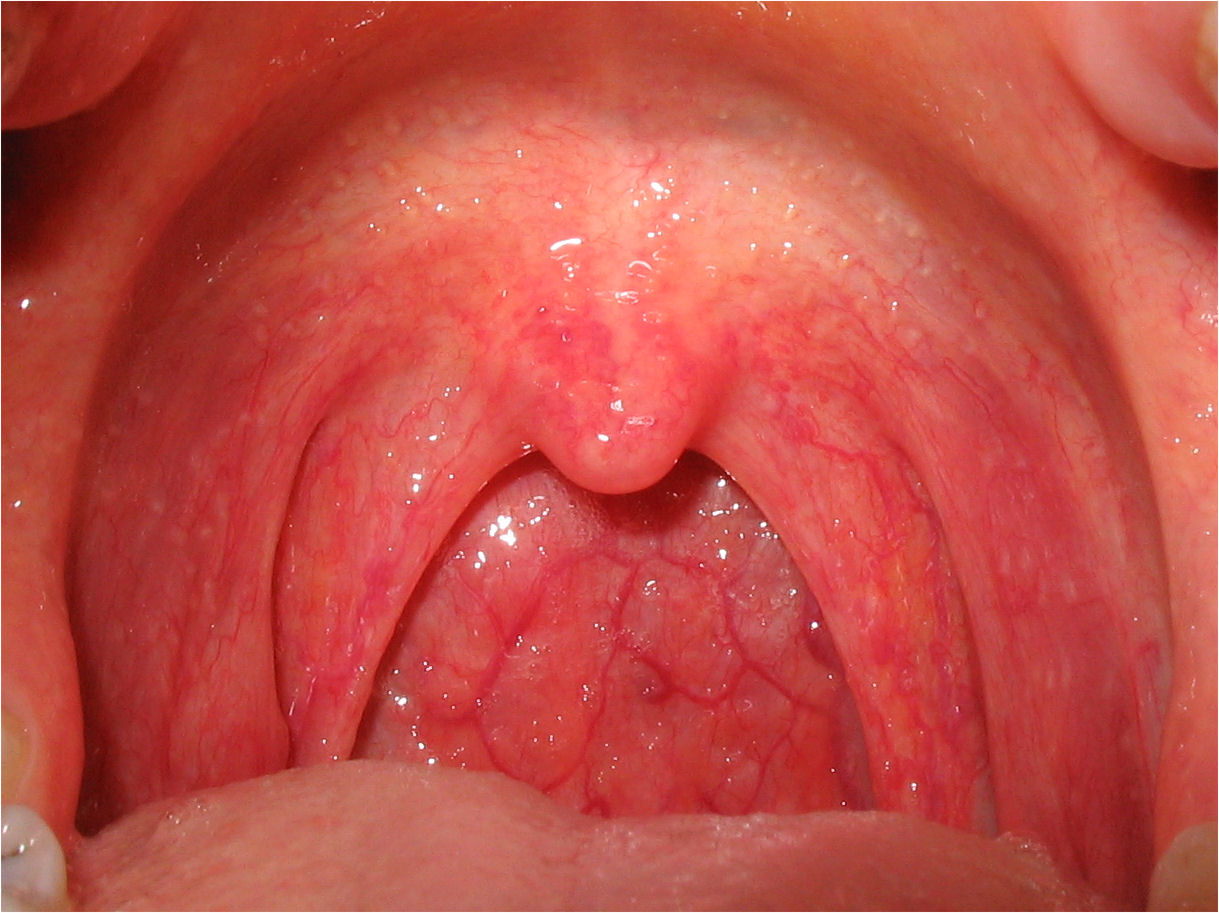
Overview Of Acute sore throat
An acute sore throat, also known as pharyngitis, is a sudden onset of pain, scratchiness, or irritation in the throat, often worsened by swallowing. It is a common condition and may be caused by infections, irritants, or other factors. --- ### **Causes**: - **Viral infections** (most common): - Common cold viruses (e.g., rhinoviruses, coronaviruses). - Influenza virus. - Epstein-Barr virus (causing infectious mononucleosis). - **Bacterial infections**: - *Streptococcus pyogenes* (Group A streptococcus), causing strep throat. - Less common bacteria such as *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* or *Mycoplasma pneumoniae*. - **Non-infectious causes**: - Allergies (e.g., pollen, dust). - Dry air, especially during winter. - Irritants like smoke, pollution, or chemicals. --- ### **Symptoms**: - Pain or scratchiness in the throat. - Difficulty or pain during swallowing. - Swollen, red tonsils (sometimes with white patches or pus). - Hoarseness or muffled voice. - Fever (common in bacterial causes). - Swollen lymph nodes in the neck. - Runny nose, cough, or fatigue (commonly associated with viral causes). --- ### **Risk_Factors**: - Close contact with someone who has an infection. - Weakened immune system. - Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke. - Seasonal changes (e.g., higher incidence in winter). --- ### **Diagnosis**: - **Physical examination**: Looking for redness, swelling, or exudates in the throat. - **Throat swab**: Rapid antigen detection test (RADT) or throat culture to identify bacterial infections like strep throat. - **Blood tests**: Occasionally used for suspected mononucleosis or other systemic illnesses. --- ### **Treatment**: - **For viral causes** (most common): - Rest and hydration. - Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen). - Warm saltwater gargles and throat lozenges. - **For bacterial causes** (e.g., strep throat): - Antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin. - Avoiding irritants (e.g., smoke, pollutants). --- ### **Prognosis**: Acute sore throat usually resolves within 7–10 days for viral causes. Bacterial infections improve quickly with antibiotics but may lead to complications if untreated. --- ### **Complications**: - Untreated strep throat can lead to: - Rheumatic fever. - Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. - Severe infections like peritonsillar abscess. - Chronic sore throat or recurrent infections. --- ### **Prevention**: - Frequent handwashing. - Avoiding close contact with infected individuals. - Using a humidifier in dry environments. - Avoiding smoking and other throat irritants. --- ### **Related_Diseases**: - Tonsillitis. - Laryngitis. - Mononucleosis. - Allergic rhinitis. --- Let me know if you need more details or specific elaboration!
Symptoms of Acute sore throat
- - Pain or scratchiness in the throat. - Difficulty or pain during swallowing. - Swollen, red tonsils (sometimes with white patches or pus). - Hoarseness or muffled voice. - Fever (common in bacterial causes). - Swollen lymph nodes in the neck. - Runny nose, cough, or fatigue (commonly associated with viral causes). --- ### Risk_Factors: - Close contact with someone who has an infection. - Weakened immune system. - Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke. - Seasonal changes (e.g., higher incidence in winter). --- ### Diagnosis: - Physical examination: Looking for redness, swelling, or exudates in the throat. - Throat swab: Rapid antigen detection test (RADT) or throat culture to identify bacterial infections like strep throat. - Blood tests: Occasionally used for suspected mononucleosis or other systemic illnesses. --- ### Treatment: - For viral causes (most common): - Rest and hydration. - Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen). - Warm saltwater gargles and throat lozenges. - For bacterial causes (e.g., strep throat): - Antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin. - Avoiding irritants (e.g., smoke, pollutants). --- ### Prognosis: Acute sore throat usually resolves within 7–10 days for viral causes. Bacterial infections improve quickly with antibiotics but may lead to complications if untreated. --- ### Complications: - Untreated strep throat can lead to: - Rheumatic fever. - Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. - Severe infections like peritonsillar abscess. - Chronic sore throat or recurrent infections. --- ### Prevention: - Frequent handwashing. - Avoiding close contact with infected individuals. - Using a humidifier in dry environments. - Avoiding smoking and other throat irritants. --- ### Related_Diseases: - Tonsillitis. - Laryngitis. - Mononucleosis. - Allergic rhinitis. --- Let me know if you need more details or specific elaboration!
Causes of Acute sore throat
- - Viral infections (most common): - Common cold viruses (e.g., rhinoviruses, coronaviruses). - Influenza virus. - Epstein-Barr virus (causing infectious mononucleosis). - Bacterial infections: - *Streptococcus pyogenes* (Group A streptococcus), causing strep throat. - Less common bacteria such as *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* or *Mycoplasma pneumoniae*. - Non-infectious causes: - Allergies (e.g., pollen, dust). - Dry air, especially during winter. - Irritants like smoke, pollution, or chemicals. --- ### Symptoms: - Pain or scratchiness in the throat. - Difficulty or pain during swallowing. - Swollen, red tonsils (sometimes with white patches or pus). - Hoarseness or muffled voice. - Fever (common in bacterial causes). - Swollen lymph nodes in the neck. - Runny nose, cough, or fatigue (commonly associated with viral causes). --- ### Risk_Factors: - Close contact with someone who has an infection. - Weakened immune system. - Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke. - Seasonal changes (e.g., higher incidence in winter). --- ### Diagnosis: - Physical examination: Looking for redness, swelling, or exudates in the throat. - Throat swab: Rapid antigen detection test (RADT) or throat culture to identify bacterial infections like strep throat. - Blood tests: Occasionally used for suspected mononucleosis or other systemic illnesses. --- ### Treatment: - For viral causes (most common): - Rest and hydration. - Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen). - Warm saltwater gargles and throat lozenges. - For bacterial causes (e.g., strep throat): - Antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin. - Avoiding irritants (e.g., smoke, pollutants). --- ### Prognosis: Acute sore throat usually resolves within 7–10 days for viral causes. Bacterial infections improve quickly with antibiotics but may lead to complications if untreated. --- ### Complications: - Untreated strep throat can lead to: - Rheumatic fever. - Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. - Severe infections like peritonsillar abscess. - Chronic sore throat or recurrent infections. --- ### Prevention: - Frequent handwashing. - Avoiding close contact with infected individuals. - Using a humidifier in dry environments. - Avoiding smoking and other throat irritants. --- ### Related_Diseases: - Tonsillitis. - Laryngitis. - Mononucleosis. - Allergic rhinitis. --- Let me know if you need more details or specific elaboration!
Risk Factors of Acute sore throat
- - Close contact with someone who has an infection. - Weakened immune system. - Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke. - Seasonal changes (e.g., higher incidence in winter). --- ### Diagnosis: - Physical examination: Looking for redness, swelling, or exudates in the throat. - Throat swab: Rapid antigen detection test (RADT) or throat culture to identify bacterial infections like strep throat. - Blood tests: Occasionally used for suspected mononucleosis or other systemic illnesses. --- ### Treatment: - For viral causes (most common): - Rest and hydration. - Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen). - Warm saltwater gargles and throat lozenges. - For bacterial causes (e.g., strep throat): - Antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin. - Avoiding irritants (e.g., smoke, pollutants). --- ### Prognosis: Acute sore throat usually resolves within 7–10 days for viral causes. Bacterial infections improve quickly with antibiotics but may lead to complications if untreated. --- ### Complications: - Untreated strep throat can lead to: - Rheumatic fever. - Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. - Severe infections like peritonsillar abscess. - Chronic sore throat or recurrent infections. --- ### Prevention: - Frequent handwashing. - Avoiding close contact with infected individuals. - Using a humidifier in dry environments. - Avoiding smoking and other throat irritants. --- ### Related_Diseases: - Tonsillitis. - Laryngitis. - Mononucleosis. - Allergic rhinitis. --- Let me know if you need more details or specific elaboration!
Prevention of Acute sore throat
- - Frequent handwashing. - Avoiding close contact with infected individuals. - Using a humidifier in dry environments. - Avoiding smoking and other throat irritants. --- ### Related_Diseases: - Tonsillitis. - Laryngitis. - Mononucleosis. - Allergic rhinitis. --- Let me know if you need more details or specific elaboration!
Prognosis of Acute sore throat
- Acute sore throat usually resolves within 7–10 days for viral causes. Bacterial infections improve quickly with antibiotics but may lead to complications if untreated. --- ### Complications: - Untreated strep throat can lead to: - Rheumatic fever. - Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. - Severe infections like peritonsillar abscess. - Chronic sore throat or recurrent infections. --- ### Prevention: - Frequent handwashing. - Avoiding close contact with infected individuals. - Using a humidifier in dry environments. - Avoiding smoking and other throat irritants. --- ### Related_Diseases: - Tonsillitis. - Laryngitis. - Mononucleosis. - Allergic rhinitis. --- Let me know if you need more details or specific elaboration!
Complications of Acute sore throat
- - Untreated strep throat can lead to: - Rheumatic fever. - Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. - Severe infections like peritonsillar abscess. - Chronic sore throat or recurrent infections. --- ### Prevention: - Frequent handwashing. - Avoiding close contact with infected individuals. - Using a humidifier in dry environments. - Avoiding smoking and other throat irritants. --- ### Related_Diseases: - Tonsillitis. - Laryngitis. - Mononucleosis. - Allergic rhinitis. --- Let me know if you need more details or specific elaboration!
Related Diseases of Acute sore throat
- - Tonsillitis. - Laryngitis. - Mononucleosis. - Allergic rhinitis. --- Let me know if you need more details or specific elaboration!
Treatment of Acute sore throat
- **For viral causes** (most common): - Rest and hydration. - Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen). - Warm saltwater gargles and throat lozenges. - **For bacterial causes** (e.g., strep throat): - Antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin. - Avoiding irritants (e.g., smoke, pollutants). --- ### **Prognosis**: Acute sore throat usually resolves within 7–10 days for viral causes. Bacterial infections improve quickly with antibiotics but may lead to complications if untreated. --- ### **Complications**: - Untreated strep throat can lead to: - Rheumatic fever. - Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. - Severe infections like peritonsillar abscess. - Chronic sore throat or recurrent infections. --- ### **Prevention**: - Frequent handwashing. - Avoiding close contact with infected individuals. - Using a humidifier in dry environments. - Avoiding smoking and other throat irritants. --- ### **Related_Diseases**: - Tonsillitis. - Laryngitis. - Mononucleosis. - Allergic rhinitis. --- Let me know if you need more details or specific elaboration!
Generics For Acute sore throat
Our administration and support staff all have exceptional people skills and trained to assist you with all medical enquiries.

Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin

Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid (Clavulanate)
Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid (Clavulanate)

Benzathine Penicillin
Benzathine Penicillin

Benzocaine
Benzocaine

Benzocaine 0.065% + Camphor 0.25% + Methanol 0.25%
Benzocaine 0.065% + Camphor 0.25% + Methanol 0.25%

Benzocaine 0.20% + Camphor 0.25% + Methanol 0.25%
Benzocaine 0.20% + Camphor 0.25% + Methanol 0.25%

Bromhexine Hydrochloride
Bromhexine Hydrochloride

Cefaclor
Cefaclor

Cefadroxil
Cefadroxil

Cefixime
Cefixime

Cefpodoxime
Cefpodoxime

Cefpodoxime + Clavulanic Acid
Cefpodoxime + Clavulanic Acid

Cefuroxime
Cefuroxime

Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.25% + Lidocaine Hydrochloride
Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.25% + Lidocaine Hydrochloride

Clindamycin
Clindamycin

Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen

Paracetamol
Paracetamol

Phenoxymethyl Penicillin
Phenoxymethyl Penicillin

Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin

Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid (Clavulanate)
Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid (Clavulanate)

Benzathine Penicillin
Benzathine Penicillin

Benzocaine
Benzocaine

Benzocaine 0.065% + Camphor 0.25% + Methanol 0.25%
Benzocaine 0.065% + Camphor 0.25% + Methanol 0.25%

Benzocaine 0.20% + Camphor 0.25% + Methanol 0.25%
Benzocaine 0.20% + Camphor 0.25% + Methanol 0.25%

Bromhexine Hydrochloride
Bromhexine Hydrochloride

Cefaclor
Cefaclor

Cefadroxil
Cefadroxil

Cefixime
Cefixime

Cefpodoxime
Cefpodoxime

Cefpodoxime + Clavulanic Acid
Cefpodoxime + Clavulanic Acid

Cefuroxime
Cefuroxime

Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.25% + Lidocaine Hydrochloride
Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.25% + Lidocaine Hydrochloride

Clindamycin
Clindamycin

Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen

Paracetamol
Paracetamol

Phenoxymethyl Penicillin
Phenoxymethyl Penicillin